Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Male flowers protrude from joints of young plants
Male flowers develop quickly on elongating stem
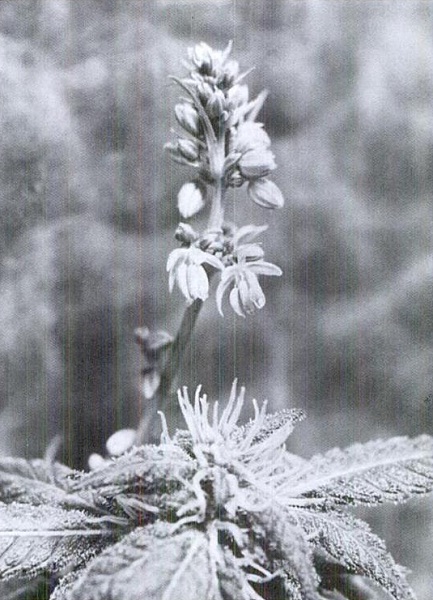
Male and female flowers
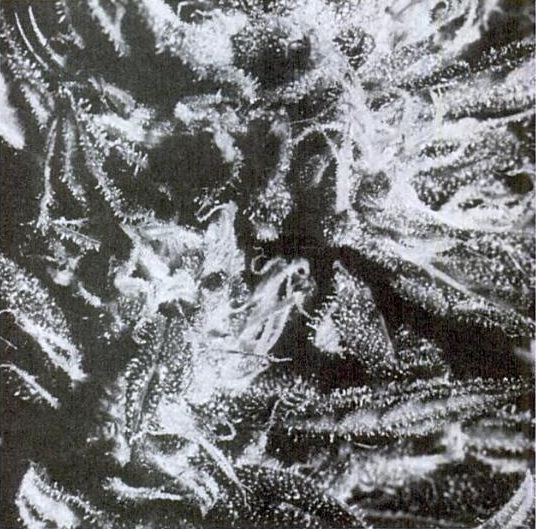
Mature female flowers
The males elongate upon ripening so that their flower sacks, which contain copious amounts of pollen, tower above the females. Marijuana is normally wind-pollinated. The females start to grow stocky stems with shorter nodes between the leaves. The number of fingers on the leaves decreases and the plant may revert from opposite leaves to a pattern of leaves alternating on the stem. Within a few weeks, large numbers of pistils (the white antennae) will form along the stem and on the tops of the branches. If the flowers are fertilized, the pistils will start to dry up, beginning at the tips. Each fertilized flower produces a seed. Such formation, which commences upon fertilization, is apparent by the third day. The ovary at the base of the pistil swells as the new seed grows inside of it. As long as most flowers remain unfertilized, the plant continues to produce new flowers. The clusters get thick with the unfertilized flowers over a period of several weeks. Then the flowering pattern begins to change. The pistils begin to wither, similar to the way pistils of fertilized flowers do and they begin to dry while at the same time changing color. Next, the calyx (ovary) begins to swell. There is no seed developing inside the calyx; it is a sort of a false pregnancy. When the calyx has swelled, the cluster or cola is ripe and ready to be picked. The pistil's color is a factor of genetics and temperature. Some plants, including many indicas, naturally develop a purplish color. Many indicas and most sativas develop a red color. However, the color may change to purple or become more pronounced if the roots are subjected to a cool environment, below 55 degrees. The growing flowers develop glands over their outer surfaces. Glands also develop along the small leaf parts surrounding the flower. These are unlike the glands found on the immature plant, the sun leaves, and the stem. The earlier glands were either connected directly to the plant, usually along the stem or had a small one-celled stalk connected to the head which filled with cannabinoids. The new glands have a longer stem which supports a larger head. The head is a membrane that fills with cannabinoids. The analogs of THC produced in the different types of glands may vary. When the gland first appears the head is small but it begins to swell and looks like it might burst. Given any stress it will. Usually the head is filled as the plants go into the last stage of flowering, as the ovaries begin to swell. This is usually when experienced growers pick the buds. Researchers, scientists, and gardeners have debated the purpose that THC serves to the plant. THC and the water-soluble com- pounds which impart the taste and aroma to the flowers act as an anti-bacterial agent, and repel some insects. They also repel most other animals including mammals and birds. (Remember, we are talking about a mature plant, heavy with resin.) This is not uncommon in plants. To assure that the seed is viable and not destroyed before it matures, the plant puts out a powerful array of chemicals to thwart predators. Once the seed matures, it is palatable to these creatures. This is one of the ways that the plant spreads its populations without human help. Animals and birds eat the seeds, an occasional seed passes out of the animal's system unharmed, allowing the species to colonize a new location. Once the calyx swells, the glands begin to change color. The THC in the head was previously a clear liquid. When the calyx is getting a little overripe, the gland head tints an amber shade. This indicates that the THC is beginning to degrade into two other cannabinoids, CBL or CBN, which are not nearly as powerful as THC.
|
||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-01-19; просмотров: 124; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.21.43.192 (0.004 с.) |