Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
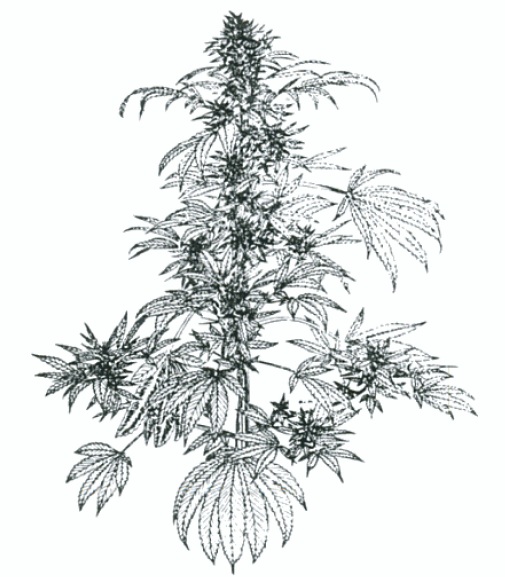
Глава 1. Растение марихуана (конопля)
Скорее всего, конопля происходит с Гималайских предгорий, хотя из-за тесных, почти симбиотических отношений с человеком точно определить её происхождение невозможно. Её выращивали ради трех основных продуктов – семян, которые используются в пищу и для получения масла, волокна – из него делали одежду и верёвки, и смолы, содержащей тетрагидроканнабиол (ТГК). Растения, которые выращивают ради семян и волокна, обычно содержат крайне малое количество ТГК и называются по-английски hemp. Разновидности с высоким содержанием ТГК называются «марихуана» (marijuana) и выращиваются исключительно с целью получения психоделических продуктов. Использование конопли и ее продуктов быстро распространилось по всему миру, сейчас её выращивают в регионах от Арктики до экватора. Она прошла сотни и тысячи поколений естественного и искуственного отбора, в результате чего имеется множество сортов, приспособленых к конкретному климату и дающих максимальное количество требуемой продукции. Конопля, которую перестают культивировать, быстро становится «дикой» и продолжает расти в естественных условиях – например, на территории Среднего Запада (Midwestern) США заросли конопли берут своё начало с заброшенных в 40-х годах плантаций. Эти заросли образует конопля, которая на протяжении многих поколений приспособилась к окружающим условиям.
Вследствие селекционной работы сейчас имеется множество различных сортов конопли, отличающихся высотой, шириной, расположением веток, размером и формой листьев, периодом цветения, продуктивностью, «пручестью», запахом и т.д. По большей части «пручесть» конопли – фактор генетический, т.е. для каждого сорта характерно свое количество смол и ТГК. Задача конопляного садовода – позволить сортам с высоким содержанием ТГК как можно полнее реализовать их потенциал. Конопля является быстрорастущим однолетним растением, однако, в некоторых тёплых регионах она может и зимовать. Лучше всего она растет на плодородных почвах, имеющих хороший дренаж. Конопля требует много солнца или мощное искуственное освещение. Обычно конопля двупола, т.е. имеются кусты как женские, так и мужские. Изредка попадаются кусты-гермафродиты, имеющие одновременно женские и мужские цветы.
В естественных условиях сроки и размер урожая зависят только от погодных условий, таких, как количество солнечных дней, уровень осадков, температура воздуха и т.д. В случае же оранжерейного культивирования условия окружающей среды полностью контролируются садоводом, что позволяет регулировать сроки цветения, созревания семян и сбора урожая.
Глава 2. Выбор сорта
Gardeners can grow a garden with only one or two varieties or a potpourri. Each has its advantages. Commercial growers usually prefer homogeneous gardens because the plants taste the same and mature at the same time. These growers usually choose fast maturing plants so that there is a quick turnaround. Commercial growers often use clones or cuttings from one plant so that the garden is genetically identical; the clones have exactly the same growth habits and potency.
Homegrowers are usually more concerned with quality than with fast maturity. Most often, they grow mixed groups of plants so they have a selection of potency, quality of the high, and taste. Heterogeneous gardens take longer to mature and have a lower yield than homogeneous gardens. They take more care too, because the plants grow at different rates, have different shapes and require varying amounts of space. The plants require individual care.
Marijuana grown in the United States is usually one of two main types: indica or sativa. Indica plants originated in the Hindu- Kush valleys in central Asia, which is located between the 25–35 latitudes. The weather there is changeable. One year there may be drought, the next it might be cloudy, wet, rainy or sunny. For the population to survive, the plant group needs to have individuals which survive and thrive under different conditions. Thus, in any season, no matter what the weather, some plants will do well and some will do poorly.
Indica was probably developed by hash users for resin content, not for flower smoking. The resin was removed from the plant. An indication of indica's development is the seeds, which remain enclosed and stick to the resin. Since they are very hard to disconnect from the plant, they require human help. Wild plants readily drop seeds once they mature.
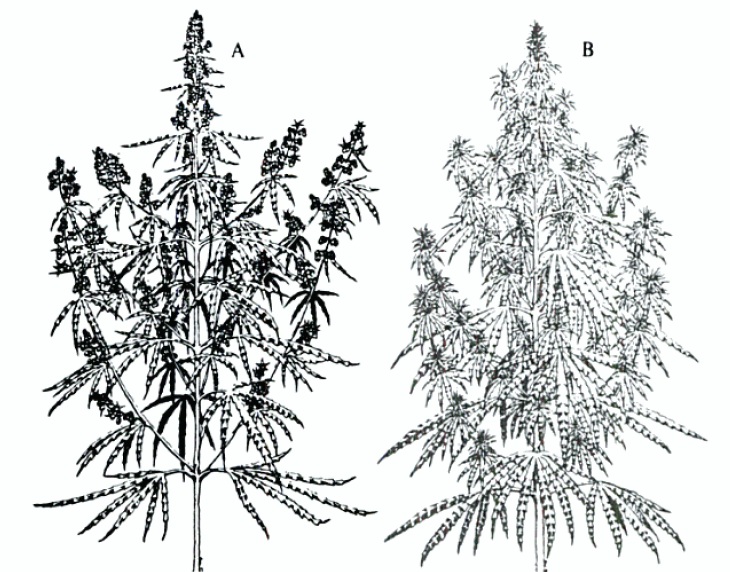
Hindu-Kush plant. The branches are short and stay close to the main stem. The center bud is very prominent. The plant uses relatively little space and has a heavy yield. This is a typical indica plant. From MARIJUANA BOTANY © 1981 by R.C.Clarke, published by And / Or? Press, Inc.
Plants from the same line from equatorial areas are usually fairly uniform. These include Colombians and central Africans. Plants from higher latitudes of the same line sometimes have very different characteristics. These include Southern Africans, Northern Mexicans, and indicas. The plants look different from each other and have different maturities and potency. The ratio of THC (the ingredient which is psychoactive) to CBD (its precursor, which often leaves the smoker feeling disoriented, sleepy, drugged or con- fused) also varies.
High latitude sativas have the same general characteristics as other sativas: conical form, long bladed leaves, wide spacing between branches, and vigorous growth.
Indicas do have some broad general characteristics: they tend to mature early, have compact short branches and wide, short leaves which are dark green, sometimes tinged purple.
Indica buds are usually tight, heavy, wide and thick rather than long. They smell “stinky”, “skunky”, or “pungent” and their smoke is thick – a small toke can induce coughing. The best indicas have a relaxing “social high” which allow one to sense and feel the environment but do not lead to thinking about or analyzing the experience.
(A) Male and (B) female Mexican plants. The plants have long spreading branches with thin, long buds. The plant uses a large space for a moderate yield. This is a typical of a sativa plant. Illustration by P. Elias from MARIJUANA BOTANY © 1981 by R.C.Clarke, published by And / Or? Press, Inc.
Cannabis sativa plants are found throughout the world. Potent varieties such as Colombian, Panamanian, Mexican, Nigerian, Congolese, Indian and Thai are found in equatorial zones. These plants require a long time to mature and ordinarily grow in areas where they have a long season. They are usually very potent, containing large quantities of THC and virtually no CBD. They have long, medium4hick buds when they are grown in full equatorial sun, but under artificial light or even under the temperate sun, the buds tend to run (not fill out completely). The buds usually smell sweet or tangy and the smoke is smooth, sometimes deceptively so.
The THC to CBD ratio of sativa plants gets lower as the plants are found further from the equator. Jamaican and Central Mexican varieties are found at the 15–2Oth latitudes. At the 3Oth latitude, varieties such as Southern African and Northern Mexican are variable and may contain equal amounts of THC and CBD, giving the smoker a buzzy, confusing high. These plants are used mostly for hybridizing. Plants found above the 3oth latitude usually have low levels of THC, with high levels of CBD and are considered hemp.
ТАБЛИЦА
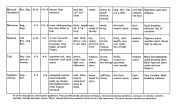
Variety Maturity Outdoor Size Branching Pattern Bud Type Aroma High Buds Color Comments (in feet) Density of Bud (flowers) Height Width Indoors Afghani mid- 4–8 3–6 squat, compact, thick, heavy heavy, rounded, dark The standard corn- & Kush Sept. short sidebranches, dense, pungent, tiring, dense green, mercial plant. Quality – Oct. thick webbed leaves short, skunky- stupefying purple varies within rounded fruity population. Colombian late7–12 4–7 conical, X-mas med. thick, sweet, spacy, Tends to run green, Rarely seen commer Nov.-Jan. tree, long branches 4–8" long, fruity, thought- long flower some red cially. Needs lots of at bottom, tapering light to light provoking, stem, sparse light and warmth to at the top, thin long medium strong flowered develop thick colas. leaves density Indian mid Nov.- 8–12 4–6 long internodes, big big, thick, med strong, large fluffy light Will run without (Central) mid Dec. leaves, strong firm 7–12" long; fruity- active, buds green, intense light. branches, elongated light-wt. skunky social red Susceptible to conical shape flowers on pistils fusarium wilt. tiny cola branches. Jamaican late 6–10 3–6 conical, but squat- long thin light, medium, thin, long runs light Adaptable, good Oct.-Dec. ter than Col. Med. colas sweet, active, under low light green weather resistance. leaves, medium w/buds musky social Susceptible to branching 11/2 “-3” fusarium wilt. long Mexican Oct.-early 8–15 41/2–9 elongated long, thin light, weak, long thin light Vigorous plants, fast (Northern) Nov. X-mas tree, long 12"-24” sweet slightly mature well green, starters. Some cold- branches, medium- colas perfume, heavy, red resistance. sized leaves spicy sleepy Mexican Nov.-Dec. 8–14 4 1/2–9 shorter than long thin sweet comes on long, thin, may very' light Hybridizes well with (Southern) northern 12 “-18” quick; run a little colored, Afghani. colas intense, red hairs soaring Moroccan Aug.- 4–9 21/2–5some sidebranching, thick, round med. weak, thin buds dark Good breeding Sept. but most effort in ed, 3"-6” sweet to buzzy mature easily green material, lots of tops long skunky variation. Nigerian mid 6–12 4–7 X-mas tree with med. thick, dry- very thick, med. medium Vigorous warm Nov.-mid strong side dense; runs sweet, strong, length, may green weather plant. Needs Dec. branches; long, in low light perfume bell- run; needs light to mature. highly serrated musk ringing, lots of light fingers paralyzing Thai Dec.-Jan. 5–9 4–8 asymmetrical, long dense, medium, strong fluffy, medium Many hermaphodites and con- branches seek open under high dry- druggy, mature Se- green make growing hard. tinuing space light runs sweet, has energ quentially Buds ripen but plant otherwise spicy over months sends out new flowers. Southern Aug.- 5–9 4–6 elongated conical med. thick, heavy uplifting, thin buds light Very variable. Good African Oct. lower branches may be sweet to social mature easily green breeding material. angle up sharply; somewhat spicy thin-bladed leaves loose & often heavily leafy serrated.
All of the descriptions are tentative guidelines. They are affected by cultivation technique, microenvironmental conditions, variations in climate, nutrients available, latitude and other factors. Often, several distinctive varieties can be found in the same areas. The most common varieties are described.
If indica and sativa varieties are considered opposite ends of a spectrum, most plants fall in between the spectrum. Because of marijuana and hemp's long symbiotic relationship with humans, seeds are constantly procured or traded so that virtually all populations have been mixed with foreign plants at one time or another.
Even in traditional marijuana-growing countries, the marijuana is often the result of several crossed lines. Jamaican ganja, for example, is probably the result of crosses between hemp, which the English cultivated for rope, and Indian ganja, which arrived with the Indian immigrants who came to the country. The term for marijuana in Jamaica is ganja, the same as in India. The traditional Jamaican term for the best weed is Kali, named for the Indian killer goddess.
Глава 3. Рост и цветение
Конопля регулирует сроки цветения в зависимости от изменения непрерывного тёмного времени суток. Она производит гормон фитохром, начиная с момента прорастания. Когда уровень этого вещества достигает порогового значения, растение переходит из режима вегетативного роста в режим цветения. Гормон разрушается во время даже очень коротких периодов освещённости. Ранней весной и летом светлое время суток гораздо длиннее тёмного, и критический уровень не достигается, но с уменьшением светлого времени суток уровень гормона растёт, и в какой-то момент растение начинает цвести. Это происходит в разное время, в зависимости от сорта конопли и окружающих условий. Конечно же, в случае оранжерейного выращивания режим освещённости менять очень просто. Как правило, сила травы гораздо больше зависит от зрелости (maturity), чем от хронологического возраста. Генетически одинаковые растения в возрасте 3 и 6 месяцев (но и то, и другое – с развившимися цветами) имеют одинаковую силу. Понятно, что более взрослое растение, как более развитое, зацветает быстрее и даёт больший урожай.
|
|||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-01-19; просмотров: 176; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.217.220.114 (0.017 с.) |