
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
First structural vector Q, eccentricities and measure of complexity
Statements formulated in the previous part allow the proposal of a variant of radical modification (changes) of structural complexity estimation Ψ(K), which is based on results of the Polyhedral Dynamics procedure. Speaking about simplicial complex K, we imply that this corresponds to complex Q= dim K, is the number of connectivity components at the dimensional level q — if two simplices are connected by a q-chain, then they are also (q-1)-,…,1-, 0-connected in complex K. According to the definition, a simplicial complex K is a collection of simplices and their faces, therefore the local properties of individual simplices in the analysis of a system’s structure are also important. In order to specify a measure of simplex’s integrity in the complex, as well as to define its role in connecting the other simplices (grouping them together in a sense of the Polyhedral Dynamics procedure) at different dimensional levels, an eccentricity characteristic was proposed. The formula for calculating eccentricity of simplex ecc(σ) = requires the dimensionality of simplex σ dim(σ) and the largest value of q for which simplex σis connected to some other simplex in complex K(q). If simplex σ gets into the same connectivity component with at least one other simplex at dimensional level q=dim(σ), then ecc(σ)=0, and this simplex is classified as «well (or strongly) integrated» in the complex K. Assuming all simplices to form one connectivity component at the dimensional level -1 (model K represents a system), a simplexσ isolated at the level q = 0 is characterized by the infinite value (∞) of eccentricity since q= −1. Vector Q can be considered as a global characteristic of simplicial complex K, but it does not characterize the complex uniquely. The latter means that two different complexes may have the same vector Q (Earl 1981), although a distinction between complexes can be revealed by studying chains of connectivity. At the same time, the axiomatically introduced estimation ΨK is calculated exactly on the basis of
If the results of Q-analysis for two different simplicial complexesare the same, then the numerical estimations Ψ( 2. Make a written translation of the following passage.
|
||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-12-30; просмотров: 270; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 52.14.240.178 (0.005 с.) |
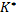 as well. A total number of vector Q elements is equal to (dimK+1) — they can be denoted as
as well. A total number of vector Q elements is equal to (dimK+1) — they can be denoted as 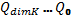 , where
, where  ,
,
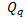 values as follows:
values as follows: , N=dimK
, N=dimK )and Ψ(
)and Ψ(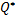 in some cases), and hence it results in «identification» of structures under study. For example, assume matrix representations of two arbitrary relations λ≤
in some cases), and hence it results in «identification» of structures under study. For example, assume matrix representations of two arbitrary relations λ≤  and
and 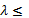
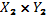 – Figure 1 shows matrices A and B in which elements of sets
– Figure 1 shows matrices A and B in which elements of sets  and
and  denote the rows. Equivalent geometric forms of corresponding complexes
denote the rows. Equivalent geometric forms of corresponding complexes  (
( and
and  (in a short notation,
(in a short notation,  ) are outwardly very similar, the only exception being that 0-simplex
) are outwardly very similar, the only exception being that 0-simplex  in complex
in complex  is a face of simplex
is a face of simplex  , while in the complex
, while in the complex  is a face of
is a face of 


