
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Digital divide: Kazakhstan's perspective
Kazakhstan is also facing the problem of digital divide, especially between the urban and rural population characterized by uneven distribution of telecommunications infrastructure. Most of the rural areas of Kazakhstan are technologically backward. People who live in the province face many difficulties which hinder their development. “The lack of infrastructure, energy grids, international bandwidth, and the high costs of access and equipment are the main constraints to providing international communication technology to the rural masses, and even to some urban centers. In addition to this basic lack of physical infrastructure, the limited human and institutional capacity, outdated or weak regulatory frameworks are common to most parts of the peripherilized territories.
Furthermore, rural economic sectors, small and medium scale industries have not been properly connected to the national and regional chains of production and services, and thereby into the global economic system” (Neville, 2003).
In order to improve the situation, Kazakhstani government has been taking some measures, like the Program for Bridging Digital Divide in the Republic of Kazakhstan. This program was adopted by Resolution of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan in October, 2007. The program’s goals are bridging digital divide in the Republic of Kazakhstan, achieving 20% computer literacy of citizens and Internet users, enhancing the value of information resources for citizens' everyday life.
This program has yielded positive results. Within two years of the Program implementation about 2 million citizens were trained, tested and certified, in collaboration with the government agencies, 8 information portals aimed at promoting ICT adoption were created, a Distance Learning Center was established, 80 certified e-courses on IT and Management were laid out on the DLC portal in Kazakh and Russian languages (Electronic Government, 2009).
The effectiveness of the measures taken may be expressly demonstrated by the growth of the number of Internet users in Kazakhstan, which is presented in the table below (Lyakhov, 2006):
So, it may be concluded that Kazakhstan is actively bridging the Digital Divide. But judging by the figures, there is a lot more to be done in this direction.
VOCABULARY FOCUS Activity 2. Give antonyms: 1) fair; 2) balance; 3) even; 4) brain; 5) enhance; 6) connected; 7) disparity; 8) urban; 9) literacy Activity 3. Mark the odd word: 1) a) hinder b) block c) oppose d) dispose 2) a) constraint b) suppression c) restriction d) limitation 3) a) imply b) hint c) comply d) presuppose 4) a) retain b) obtain c) acquire d) get 5) a) bring about b) cause c) result in d) result from 6) a) gap b) divide c) break d) gaze 7) a) accumulate b) select c) bring together d) collect
Activity 4. Match the words with their collocations:
GRAMMAR FOCUS Activity 5. Identify the italicized –ed verb forms as a part of the predicate (P) or an attribute (A):
1) The term was first used by the UN ICT Task Force, created after the 2003 Summit in Geneva. 2) Digital divide means the difference in access to ICTs between developed and developing countries. 3) All above mentioned can lead to a digital divide. 4) Countries with developed information technologies will acquire new values and lose old ones. 5) Consumers who are isolated from this commodity will be concentrated in another part of the world. 6) Kazakhstan is also facing the problem of digital divide, especially between the urban and rural population characterized by uneven distribution of telecommunications infrastructure. 7) The limited human and institutional capacity, outdated or weak regulatory frameworks are common to most parts of the peripherilized territories. 8) This program has yielded positive results. 9) There were created 8 information portals aimed at promoting ICT adoption.
Activity 6. Open the brackets: 1) Uneducated people (unlikely, be interested) in IT. 2) For example, music (create and transfer) in digital form. 3) With the time, the flow of cheap commodities (concentrate) in one part of the world. 4) In rural economic sectors, small and medium scale industries (not yet properly connect) to the national and regional chains of production and services. 5) Within two years of the Program implementation about 2 million citizens (train, test and certify). 6) The growth in the number of Internet users in Kazakhstan (present) in the table below. 7) So, it may (conclude) that Kazakhstan (actively bridge) the Digital Divide 8) In order to improve the situation, the RK government (take) some measures lately. WHILE-READING Activity 7. Mark the statements as True or False: 1) Digital divide concerns mostly relationships between different countries. ___ 2) The term “infrastructure” implies available facilities and equipment. ___ 3) One of the causes of digital divide is brain drain. ___ 4) The richer the country, the lower are the connectivity costs. ___ 5) There is a digital divide between urban and rural population in Kazakhstan. ___
Activity 8. Fill in the table with the information from the text on the digital divide causes, consequences and solutions. Add your own ideas.
POST-READING Activity 9. Translate the first paragraph of the text. Activity 10. Think of some possible consequences of not bridging the digital divide in our country. Activity 11. Group competition. Suggest some ideas to bridge the digital divide in Kazakhstan. Vote for the group with the best suggestions.
Activity 12. Watch the video “ What does the digital divide mean to you?” (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fCIB_vXUptY&playnext=1&list=PL6200B4A32A12F8A8&feature=results_main) and answer the following questions: 1) What do people need to get online? 2) How many Americans do not have access to the Internet? 3) What are the major factors which affect the Internet connection figures in the US? 4) How would a 1% increase in broadband capacity affect the labor market? 5) What for do Americans need Internet access for? MODULE 3. LEGAL FOCUS TARGET VOCABULARY
TARGET VOCABULARY QUIZ
Choose the correct answer: 1. A type of software that collects information from your computer without your consent is called _____. a) spyware b) adware c) malware d) freeware 2. _____ is the virtual world of computer and the Internet. a) Site b) Chat room c) Forum d) Cyberspace 3. The process of saving and transmitting data into a secret code is called _____. a) decoding b) decryption c) encryption d) conversion 4. Software, created to damage computer data is called _____. a) adware b) malware c) spyware d) freeware 5. Internet-based conflict involving politically motivated attacks on information and information systems is called cyber_____. a) warfare b) crime c) hacking d) attack 6. _____ is an illegal way of getting money via e-mail by promising profits from investing in a business activity which does not really exist. a) Piracy b) Scam c) Phishing d) Skimming 7. All of these are synonyms EXCEPT for: a) encode b) encrypt c) code d) decipher 8. _____ is a self-replicating computer virus that penetrates an operating system with the intent of spreading malicious code. a) Virus b) Trojan horse c) Worm d) Logic bomb 9. All of these are synonyms EXCEPT for: a) intruder b) invader c) hacker d) cracker 10. _____ is someone who invades a network’s privacy. a) Hacker b) Invader c) Cybersquatter d) User 11. A _____ is a software and/or hardware device that allows limited access to an internal network from the net. a) protocol b) cookie c) firewall d ) f irework 12. Digital _____ is a file that identifies a user or a web server. a) document b) certificate c) card d) signature 13. All of these are computer crimes EXCEPT for: a) scam b) phishing c) piracy d) cyber warfare 14. Cyber_____ is the illegal use of the Internet, email, or other electronic communication systems to follow or threaten someone. a) stalking b) surfing c) slacking d) loafing 15. To do something that is against a law or someone's legal right means to _____ it. a) copyright b) destroy c) break d) infringe on 16. To say false things about someone in order to damage his reputation means to _____. a) accuse b) slander c) abuse d) harass 17. All of these go with the word “security” EXCEPT for: a) hole b) flaw c) backdoor d) breach 18. ______ is a computer program that detects and records a variety of restricted information. a) Sniffer b) Adware c) Malware d) Anti-spam 19. A computer program which must be physically copied is called a_____. a) worm b) Trojan horse c) virus d) logic bomb 20. There is infringement _____ privacy due to the development of social networks and other similar services. a) with b) in c) at d) on TEXT 1. COMPUTER CRIME Compiled by A. Sholakhova R. Esteras, Elena M. Fabré. Professional English in Use. Cambridge University Press, 2007. p. 62 (http://www.rbs2.com/ccrime.htm,
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/types-of-computer-crimes.html)
www.itp.net PRE-READING Activity 1. What is cybercrime? Have you ever come across any? Computer crime is a criminal activity involving the use of information technology to gain an illegal or an unauthorized access to a computer system with intent of damaging, deleting or altering computer data. People who commit crimes using computers are often called computer hackers or crackers. In the computer industry, hackers are known as white hats and crackers are called black hats or dark side hackers. White Hat hackers are those people who attempt to hack into, or break into, computers and computer programs with the intent of finding things that are wrong and fixing them to help the computer owner. Black Hat hackers are those people who break into computer systems with malicious intent – usually to steal or vandalize.
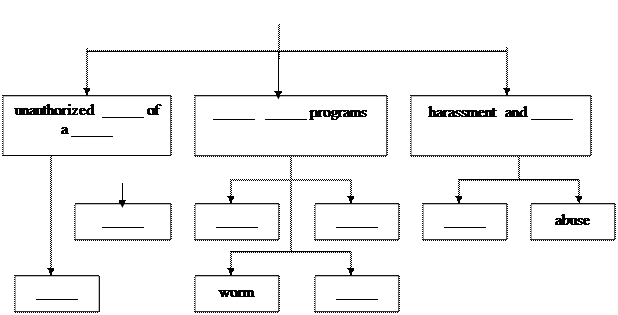
There are three major classes of computer crimes: 1. unauthorized use of a computer, which might involve stealing a username and password (e.g. piracy, scam, phishing); 2. creating or releasing a malicious computer program (e.g. computer virus, worm, Trojan Horse); 3. harassment and cyberstalking. Internet piracy involves the downloading and distribution of copyrighted media without paying for it. When people download or copy content such as music, books, games and other digital media, they may be infringing on copyright laws. Phishing is a bank fraud to get banking information such as passwords of Internet bank accounts or credit card details. Criminals often use websites that have a look and feel of some popular websites, which make the users feel secure. Scam is email fraud to obtain money or valuables.
Malicious program is a general term for any computer program that is designed to harm its victim(s). Malware (malicious software) is software created to damage or alter the computer data or its operations. These are the main types of malware: · Viruses are programs that spread by attaching themselves to executable files or documents. When the infected program is run, the virus propagates to other files or programs on the computer. Some viruses are designed to work at a particular time or on a specific date, e.g. on Friday 13th. An email virus spreads by sending a copy of itself to everyone in an email address book.The word "virus" is also used broadly to include computer viruses, worms, and Trojan Horse programs. · Worms are self-copying programs that have the capacity to move from one computer to another without human help, by exploiting security flaws in computer networks. Worms are self-contained and don't need to be attached to a document or program the way viruses do.
People often confuse viruses and worms. Some confusion about the distinction between a virus and a worm is caused by two distinctly different criteria: 1. a virus infects an executable file, while a worm is a stand-alone program. 2. a virus requires human action to propagate (e.g., running an infected program, booting from a disk that has infected boot sectors) even if the human action is inadvertent, while a worm propagates automatically. · Trojan horses are malicious programs disguised as innocent-looking files or embedded within legitimate software. Once they are activated, they may affect the computer in a variety of ways: some are just annoying, others are more ominous, creating a backdoor to the computer which can be used to steal data. They don't copy themselves or reproduce by infecting other files. · Spyware, software designed to collect information from computers for commercial or criminal purposes, is another example of malicious software. It usually comes hidden in fake freeware or shareware applications downloadable from the Internet.
Due to its anonymity, the Internet provides the right environment for cyberstalking,online harassment (sending threatening email messages and slandering people) or abuse, mainly in chat rooms. False accusations and transmission of threats fall under the class of cyberstalking activities.
There is a large number of ways that can be used to protect your computer from all these threats: · Use strong passwords (at least eight characters long). · Don't open email attachments from unknown people; always take note of the file extension. · Run and update antivirus programs, e.g. virus scanners. · Install a firewall, a program designed to prevent spyware from gaining access to the internal network. · Make backup copies of your files regularly. · Stay away from untrusted networks. · Use a digital certificate, an electronic way of proving your identity, when you are doing business on the Internet. Avoid giving credit card numbers. · Don't believe everything you read on the Net. Have a suspicious attitude toward its contents. VOCABULARY FOCUS Activity 2. Choose the correct answer: 1. “Vandalize” means all of these except for: a) damage b) destroy c) break d) steal 2. _____ file is one which contains a set of code written to run/create a program. a) Executable b) Attached c) Backup d) Expanding 3. “Embedded within” software means the one which is _____.
a) changed b) integrated c) converted d) connected 4. Fake freeware is the one which is _____. a) forged b) free c) trial d) genuine 5. “Propagate” means all of these EXCEPT for: a) spread b) transmit c) agitate d) disseminate 6. “Ominous” means all of these EXCEPT for: a) threatening b) dangerous c) sinister d) annoying 7. White Hat and Black Hat crackers differ in: a) qualification b) goal c) color d) clothing Activity 3. Match the words to their meanings:
Activity 4. Form collocations from columns 1 and 2, and find their definitions in column 3:
GRAMMAR FOCUS Activity 5. Define non/identifying relative clauses. Put commas where necessary. 1) The criminal who stole personal details of thousands of Internet users was finally caught yesterday. 2) Paul downloaded a malicious program which infected his computer with a virus. 3) Someone stole my credit card details which were used to pay for things on the Internet. 4) What is being done at the moment to stop cyber criminals who steal money? 5) People who commit crimes using computers are called computer hackers. 6) Hackers who break into computer systems with malicious intent steal sensitive information. Activity 6. Combine two sentences using relative pronouns and adverbs: 1) Virus is a computer program. It can make copies of itself. 2) That’s the man. His computer was crashed because of a virus. 3) Hacker is a person. He gets into someone else's computer system without permission to do something illegal. 4) Malicious program is any computer program. It is designed to harm its victim(s). 5) Harassment is behavior. Its aim is to trouble or annoy someone. 6) There is a backdoor to the computer. It can be used to steal data. 7) The Internet is a global system. You can find a lot of information there. Activity 7. Put the following adjectives in the correct column: authorized, legal, safe, secure, advertent, trusted, reliable, known, faithful, authentic, disguised, protected, altered, intentional, violate, offensive, limited, damaged, dependent
WHILE READING Activity 8. Read the text and mark the statements true (T), false (F) or not given (NG): 1) The text focuses on significant increase in the number of data-stealing attacks. ___ 2) There is no difference between viruses and worms. ___ 3) Phishing refers to cyberstalking activities. ___ 4) Harassment is the behavior intended to trouble or annoy someone. ___ 5) Worm neither deletes nor changes files on the victim's computer. ___ 6) Viruses, worms and Trojan horses constitute one group. ___ Activity 9. Which computer crimes are the following characteristics associated with:
Activity 10. Enumerate: 1) Computer crimes meant to steal information: 2) Computer crimes meant to damage data and equipment: 3) Malicious computer programs: 4) Unauthorized uses of a computer: 5) Computer crime effects: 6) Ways to protect your computer from threats:
Activity 11. Identify the Internet crimes: 1) Crackers try to find a way to copy the latest game or computer program. 2) A study has revealed that half a million people will automatically open an email they believe to be from their bank and send off all their security details. 3) The danger of this software is hidden behind an attractive appearance. That's why it is often wrapped in attractive packages promising photos of celebrities. 4) There is a particular danger in Internet commerce and emails. Many people believe they have been offered a special gift only to find out later they have been deceived. 5) “Nimda” spreads by sending infected emails and is also able to infect websites, so when a user visits a compromised website, the browser can infect the computer. 6) Every day millions of children spend time in Internet chat rooms talking to strangers. But what many of them don't realize is that some of the surfers chatting with them may be sexual predators.
Activity 12. What computer crime above does each advice refer to? a) Don’t buy cracked software or download music illegally from the Internet. b) Be suspicious of wonderful offers. Don't buy if you aren't sure. c) Don’t give personal information to people you contact in chat rooms. d) Don’t open the attachments from people you don't know even they look attractive. e) Scan your email and be careful about which websites you visit. f) Check with your bank before sending information. POST-READING Activity 13. Fill in the gaps in the graph below and speak on each item.
Activity 14. Answer the following questions: 1) Is cybercrime dangerous? Explain why/not. 2) Do you feel protected from computer crime? 3) Which security measures do/should you take against computer crime?
Activity 15. Watch the video “What is a Hacker?” ( http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0qgN4maRQdQ)and: 1) enumerate the types of hackers; 2) describe the aim of each hacker. Activity 16. Watch the video “Computer Viruses and Threats Explained - TechnoGeeks” ( http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t0M55k8Trq4) and explain the diffrences between viruses, worms and Trojan Horses.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-12-09; просмотров: 1447; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.134.81.206 (0.198 с.) |
 (v)
(v)
 (n);
syn. penetrate
(n);
syn. penetrate






