Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Duties of the President and Vice-PresidentСтр 1 из 5Следующая ⇒
UNIT I I. US GOVERNMENT 1. Read and translate the text: The USA is a presidential republic. The legislative branch of the US Government, or the Congress, represents all of the American states. It consists of two parts: the House of Representatives and the Senate. Each state has two senators, who are elected every 6 years. The job of the Congress is to make laws. The President can veto a bill. The Congress can pass the law anyway if it gets a two-thirds majority vote. The Congress can also declare war. The House of Representatives can also impeach the President. This means that the house can charge the President with a crime. In this case, the Senate will put the President on trial. The Senate votes to approve the justices that the President appoints to the Supreme Court. The executive branch of the government puts the country laws into effect. The President of the United States is a member of the executive branch. The President is elected every four years and cannot serve more than two terms. The Vice-President of the USA is a president of the Senate. When the President receives a bill from the Congress, he must sign it, and then the bill becomes a law. However if he disagrees with the law, he can veto it. The President can also ask the Congress to declare war. He also appoints the justices to the Supreme Court. He must do his job according to the Constitution, or he may be impeached. The judicial branch of the government is the system of courts in the United States. Its job is to enforce laws. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the country. It consists of 9 justices: one Chief Justice and 8 Associate Justices. The President appoints justices but the Senate must approve them. The judicial branch works together with the legislative and executive branches to protect the Constitution and the rights of people. Vocabulary: the House of Representatives- Палата представителей the Senate- Сенат to impeach the President- подвергнуть президента импичменту to charge- обвинить в каком-либо преступлении a term- срок полномочий the Supreme Court- Верховный Суд Chief Justice- Главный Судья Associate Justice- Член Верховного Суда
2. Make up your own sentences with the following verbs. You may use the text: to elect; to appoint; to sign; to consist; to become; to vote.
3. Finish the sentences according to the text: 1. The job of the Congress is…………………………………………. 2. The President appoints…………………………………………….. 3. The Senate votes.…………………………………………………... 4. The Supreme Court is……………………………………………… 5. The Supreme Court consists of…………………………………..... 6. The judicial branch is………………………………………………
4. Find the English equivalents for: - представлять; - накладывать вето на законопроект; - приводить в действие; - объявить войну; - привлечь к суду (судебному разбирательству); - проводить закон в жизнь; - назначать.
5. Answer the questions: 1. What branches does the government of the USA consist of? 2. Who does the highest executive power belong to? 3. Who represents the legislative power in the USA? 4. What is the judicial branch of the government? What is its job? 5. What can you say about the Supreme Court of the USA?
6. Speak on: 1. The government in your country.
II. EXECUTIVE BRANCH: PRESIDENT, VICE-PRESIDENT AND THE CABINET
1. Read and translate the text: The executive branch, which includes the President, the Vice-President and the Cabinet consisting of Secretaries of the executive departments, is responsible for administering and executing the laws.
If the President dies, or resigns, or can’t work, the Vice-President becomes the President. So the qualifications for the Vice-President are the same as for the President. Within the Executive Branch, there are 14 executive departments. These are: the Departments of State, Treasury, Defense, Justice, Interior, Agriculture, Commerce, Labour, Health and Human Services, Housing and Urban Development, Transportation, Education, Energy, and Veteran Affairs. Each department is established by law and is responsible for a specific area. The heads of the executive departments are Cabinet members, they are appointed by the President. These appointments, however, must be approved by the Senate. All the Secretaries of the executive departments make up the Cabinet and are Presidential assistants and advisors.
Vocabulary notes:
1. Complete the scheme below according to the information given above and try to retell the text. UNIT II I. US CONSTITUTION I
"We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, ensure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America." — Preamble to the Constitution.
1. Read and translate the text: The form of the US government is based on the Constitution of 1787 which was adopted after the War of Independence. A constitution is a set of customs, traditions, rules and laws that sets forth the basic way a government is organized and functions. According to this definition of the word, every nation has a constitution but in some countries constitutions are very easily violated because the basic rights of their citizens are violated. It is very important to understand that having a constitution does not mean that a nation has a constitutional government. If a constitution makes it possible to concentrate power by one or few, it is not the basis of a constitutional government. If a constitution says that the government’s power should be limited but doesn’t mention the ways how to do it, it is not the basis for a constitutional government. In a constitutional government the constitution is a form of higher law that must be obeyed by everyone including those in power. The US Constitution consists of 7 articles and 26 amendments. According to the Founders of the American state a constitution or higher law should have the following characteristics: - It sets forth the basic rights of citizens to life, liberty and property - It establishes the responsibility of the government to protect those rights - It establishes limitations on how those in government may use their powers with regard to - citizens’ rights and responsibilities - the distribution of resources - the control of conflict - It establishes the principle of a private domain – which means that there are areas of citizens’ lives that are no business of the government and in which the government cannot interfere. - It can be changed with the consent of the most citizens. This is how the Constitution differs from the ordinary law that the governments regularly create and enforce. The US Constitution has 26 amendments, the first 10 are called the Bill of Rights and it was adopted in 1791. The bill enumerated basic freedoms and guaranteed them and declared what the government was not allowed to do.
Notes to the text: “We the People of the United States, in order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, ensure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings of Liberty to ourselves and our Posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America.”- Preamble to the Constitution – “ Мы, народ Соединенных Штатов, в целях образования более совершенного Союза, утверждения правосудия, обеспечения внутреннего спокойствия, организации совместной обороны, содействия общему благосостоянию и обеспечения нам и нашему потомству благ свободы, учреждаем и принимаем эту Конституцию для Соединенных Штатов Америки. ”- Преамбула к Конституции.
Vocabulary: a set- свод basic freedoms, rights- основные свободы, права to obey- повиноваться, выполнять to set forth- излагать private domain- личная свобода distribution of resources- распределение ресурсов
2. Give the Russian words with the same stem: base; constitution; tradition; to form; principle; to guarantee; to concentrate; nation; to control.
3. Find the English equivalents for: - справедливость; - спокойствие; - благосостояние; - благо; благодеяние; - потомство; потомки; - свод законов, правил, традиций; - принять конституцию; - поправка к Конституции; - нарушать закон; - согласие большинства; - вмешиваться; - перечислять; - выполнять, исполнять закон.
4. Express your agreement or disagreement with each statement using: I quite /completely agree, I can’t agree, I think it is not so, it’s wrong, on the contrary. 1. The American Constitution was adopted after the Warof Independence and it remains unchanged so far. 2. The US Constitution consists of 10 articles and 50 amendments. 3. The US Constitution guarantees freedom of those in power.
5. Write these sentences in the Passive Voice form and translate them into Russian: 1. The USA adopted the Constitution in 1787. 2. The Constitution provides the set of rules, laws and regulations to regulate the work of the government. 3. Some historians regard the Constitution as a conservative document. 4. In some countries the oligarchy can control the government.
6. Read the text without a dictionary and try to catch the main idea: The Amendment Process We have a living Constitution. Men wrote it in 1787, and we still use it today. These men were intelligent. “The U.S will change in the future “they thought. “We must find the way to let the Constitution change too.” And they did. They put in the amendment process. This process is important. Amendments can change the part of an article in the Constitution or another amendment. Two/thirds (2/3) of the Congress or of the state legislature must agree on an idea for an amendment. If three-fourth (3/4) of the states ratifies the amendment, it becomes a part of the Constitution.
7. Answer the questions: 1. What does a “constitution” mean in American political language? 2. What is the aim of the US Constitution? 3. What does it consist of? 4. What is the Bill of Rights? 5. What do you think about the peculiarities of the US Constitution?
8. Read and translate the text: US CONSTITUTION II The former colonies, now “the United States of America”, first operated under the agreement called the Articles of Confederation (1781). It was soon clear that this loose agreement among the states was not working well. The central, federal government was too weak, with too few powers for defence, trade and taxation. In 1787, therefore, delegates from the states met in Philadelphia. They wanted to revise the Articles, but they did much more than that. They wrote a completely new document, the Constitution, which after much argument, debate, and compromise was finished in the same year and officially adopted by the thirteen states by 1790. The Constitution, the oldest still in force in the world, sets the basic form of government: three separate branches, each one having powers (“checks and balances”) over the others. It specifies the powers and duties of each federal branch of government, with all other powers and duties belonging to the states. The Constitution has been repeatedly amended to meet the changing needs of the nation, but is still the “supreme law of the land”. All governments and governmental groups, federal, state, and local must operate within its guidelines. The ultimate power under the Constitution is not given to the President (the executive branch), or to the Supreme Court (the judicial branch). Nor does it rest, as in many other countries, with a political group or party. It belongs to “We the People, in fact and in spirit”. They stated in the first ten Constitutional Amendments, known together as the Bill of Rights, what they considered to be the fundamental rights of any American. Among these rights are the freedoms of religion, speech, and the press, the right of peaceful assembly, and the right to petition the government to correct wrongs. Other rights guarded the citizens against unreasonable searches, arrests, and seizures of property, and established a system of justice guaranteeing orderly legal procedures. This included the right of trial by jury that is, being judged by fellow citizens. The federal and state governments formed under the Constitution were designed to serve the people and to carry out their majority wishes (and not the other way around). One thing they do not want their government to do is to rule them. Americans expect their government to serve them and tend to think of politicians and governmental officials as their servants. This attitude remains very strong among Americans today. Over the past two centuries, the Constitution has also had considerable influence outside the United States. Several other nations have based their own forms of government on it. It is interesting to note that Lafayette, a hero of the American Revolution, drafted the French declaration of rights when he returned to France. And the United Nations Charter also has clear echoes of what once was considered a revolutionary document. Vocabulary: an agreement- соглашение loose agreement- свободное соглашение taxation- налогообложение freedom of religion; speech; press- свобода вероисповеданий; слова; печати unreasonable search; arrest- необоснованный обыск; арест strong attitude- жесткая позиция United Nations Charter- Устав ООН (Организации Объединенных Наций) ultimate power- необоснованно большая власть
9. Complete the following text with the words and phrases using them in the appropriate form (you may use the text above): jury; branch; Bill of Rights; to adopt; religion; to guard; power; Congress; to divide; amendments; to assemble; citizens; President; arrests; executive; rights; seizures; document; speech; legislature; freedoms; judiciary; founding fathers; system of.
When the Constitution was written in 1787, there were only 13 states. Because the a) ____ of the Constitution saw that the future might bring a need for changes, they b) ____ a method of adding c) ____. Over the years 26 amendments have been added, but the basic d) ____ has not been written. The pattern of government planned so long ago for 13 states today meets the needs of 50 states. The first 10 amendments to the Constitution, called the e) ____ assure individual f) ____ and g) ____. Added in 1791, they include provisions for freedom of the h) ____ and of i) ____; the right of citizens to j) ____ peacefully; the right to be k) ____ in one’s own home against unreasonable l) ____ and m) ____ of person or property; the right of any person charged with n) ____ the law to have a speedy trial by a o) ____ of fellow p) ____. The Constitution q) ____ the powers of the government into three branches: the r) ____ headed by the s) ____; the t) ____, which includes both houses of u) ____ (the Senate and the House of Representatives) and the v) ____ which is headed by the Supreme Court. The Constitution limits the role of each w) ____ to prevent any one branch from gaining undue x) ____.
10. Find the English equivalents for: - пересмотреть документ; - действовать в соответствии с соглашением; - управлять своими собственными делами; - принять конституцию; - определить чьи-либо полномочия и обязанности; - действовать в рамках конституции; - получить необоснованно большую власть; - свобода собраний; -захват собственности; - удовлетворять требованиям; - суд присяжных заседателей; - влияние; - отголосок.
11. Speak on: 1. The Constitution of your country.
II. THE BILL OF RIGHTS 1. Read and translate the text: On December 1791, the Congress put in the amendment process and adopted 10 amendments to the Constitution, known as the Bill of Rights. Amendments can change or add rights and restrictions to the Constitution. Amendment 1. Freedom of Religion, Speech, the Press and Assembly
Amendment 2. The Right to Have Guns We can have guns for protection. State governments make laws about buying and keeping guns. Amendment 3. No Soldier shall, in time of peace be quartered in any house, without the consent of the Owner, nor in time of war, but in a manner to be prescribed by law.
Amendment 4. Searchers and Warrants Police need a court order (search warrant, issued by a judge) to make any search or any arrest. Amendment 5. Rights of People Accused of a Crime, and Protection of Private Property. No person shall be deprived of life, liberty or property, without due process of law. No person shall be compelled in any criminal case to be a witness against himself. Amendment 6. Right to a Fair Trial and Witness. If you are accused of a crime, you have the right to know why. You have the right to a speedy and public trial with a jury. You have the trial in the state where the crime happened. You can have the private lawyer or the court will give you a lawyer. Amendment 7. Assures trial by jury in civil cases. Amendment 8. Bails, Fines and Punishment A judge cannot make you pay an unfair bail or an unfair fine. A judge or jury or the police cannot give you unfair punishment. Amendment 9. The People Keep Some Right The Constitution lists many rights of the people, but it doesn’t list all the rights. The People have other rights, too. Amendment 10. The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people. Amendments 11-26 Amendment 11. Citizens of one state or a foreign country cannot bring a case against another state in a federal court. Amendment 12. We elect the President and Vice-President separately. Amendment 13. There is no more slavery in the U.S. Amendment 14. All people born or naturalized in the U.S. are citizens. Amendment 15. Black people have the right to vote. Amendment 16. Congress can make a law for an income tax. Amendment 17. We elect Senators directly with our votes. Amendment 18. Prohibition of intoxicating liquors. Amendment 19. Women have the right to vote. UNIT III. I. MAJOR POLITICAL PARTIES 1. Read and translate the text: The United States began as a one-party political system. George Washington and many others among the Revolutionary leaders wanted it to stay that way. In 1787, when the Constitution was written, the people were divided over whether to ratify it, although they were not yet organized into definite political parties.
The parties chose their own names, Republican and Democratic, but not their party emblems. The cartoonist Thomas Nast invented the Republican elephant and the Democratic donkey in the early 1870s, and they soon became fixed types. The differences between these two parties are so small that a voter will see no intellectual inconsistency in voting for a Republican President, a Democratic state governor, a Republican Senator and a Democratic member of the House. How is an individual’s party affiliation determined, or how does a person choose sides in the game of party politics? The first and perhaps the most important determinant is family tradition. Most voters take the party of their parents. Recently there has been an increasing tendency for the well-to-do to vote the Republican Party and for the less fortunate to vote the Democratic Party. National origin plays the role too; descendants of northern Europeans tend to the Republican Party, while those of southern and eastern Europeans prefer the Democratic Party. The traditional bipartisan system is highly cherished by Big Business, for it creates a sort of illusion that voters are free to choose between the candidates of these two parties, whereas both of them faithfully serve Big Business interests. Many people say that there is not much difference between the Republican and Democratic Parties. “Liberal” politicians usually favor reforms and progress. “Conservative” politicians usually oppose changes. Both liberal and conservative members belong to the two major political parties, and their ideas are often changed with the times and the issues. Vocabulary: one-party system- однопартийная система bipartisan system- двухпартийная система city folk- городское население country folk- сельское население inconsistency- несовместимость; противоречие affiliation- присоединение to cherish- лелеять 2. Give the English equivalents for: - ратифицировать; - средний класс; - потомок; - на партийном уровне. 3. Match each word on the left with the right definition on the right:
4. Answer the questions: 1. What kind of system was characteristic of the United States at the time of George Washington? 2. What were the first reasons of people’s division into political parties? 3. Whom did the Federalists represent? 4. Who were the Republicans? 5. What are the party emblems and who invented them? 6. What distinguishes the two parties? 6. Read the text without a dictionary. Try to catch the main idea: The Democratic Party is the oldest party in the United States. In 1829, Andrew Jackson became the first Democratic President. Since that time, the issues of the nation and the ideas of the party have changed. Both the major parties have liberal and conservative members but in general people consider the Democrats today more liberal than the Republicans.
The Republican Party, sometimes called the G.O.P. (the Grand Old Party), began in 1854 over the issue of slavery. Republicans oppose slavery. The first Republican candidate to become President was Abraham Lincoln. After the Civil War, Republicans got interested in farm, land, and business issues. In general, Republicans vote more conservatively than Democrats. They want government to support big business but not to control the lives of citizens. They often oppose government spending for social programs but support military spending. The party symbol is the elephant. Vocabulary: nuclear weapon- ядерное оружие military spending- расходы на вооружение
Notes to the text: G.O.P. (the Grand Old Party) - великая старая партия (неофициальное название Республиканской партии США)
6. Say what party is spoken about in each sentence: 1. It is the oldest political party in the United States. 2. It is sometimes called the G.O.P. 3. Its first President was Abraham Lincoln. 4. Its first President was Andrew Jackson. 5. It is generally more liberal than the other party. 6. Its members usually prefer to spend tax money for military purposes rather than for social programs. 7. Its members do not want the government to control the lives of individuals. 8. The party symbol is the donkey.
7. Speak on: 1. The political parties in your country.
II. ELECTIONS 1. Read and translate the text: Anyone who is an American citizen, at least 18 years of age, and is registered to vote may vote. Each state has the right to determine registration procedures. A number of civic groups, such as the League of Women Voters, are actively trying to register as many people as possible. Voter registration and voting among minorities has dramatically increased during the last twenty years, especially as a result of the Civil Rights Movement. There is some concern, however, about the number of citizens who could vote in national elections but do not. In the national elections of 1984, for instance, only 57.4 per cent of all those who could have voted actually did. In 1992 it was 61.3. But then, Americans who want to vote must register, that is to put down their names in register before the actual elections take place. There are 50 different registration laws in the US- one set for each state. In the South, voters often have to register not only locally but also at the county seat. In European countries, on the other hand, “permanent registration” of voters is most common. Of those voters in the United States who did register in the 1988 Presidential elections, 86 per cent cast their ballots, in 1992- 89.8 per cent. The National Presidential elections consist of two separate campaigns. One is for the nomination of candidates at national party convention; the other is to win the actual election. The first stage is called “primaries”. The party convention votes to select the party’s official candidate for the presidency. Then Presidential campaigns by the candidates start. In November of the election year (years divisible by four, e.g. 1988, 1992, 1996, etc.), the voters across the nation go to the polls. If the majority of the popular votes in a state go to the Presidential (and vice-presidential) candidate of one party, then that person is supposed to get all of that state “electoral votes”. These electoral votes are equal to the number of Senators and Representatives each state has in the Congress. The candidate with the largest number of these electoral votes wins the election. Each state’s electoral votes are formally reported by the “Electoral College”. In January of the following year, in a joint session of Congress, the new President and Vice-President are officially announced. Vocabulary: a county- избирательный округ party convention – партийный съезд “Electoral College”- коллегия выборщиков nomination- выдвижение кандидата to cast a ballot- проголосовать
2. Find the English equivalents for: - зарегистрироваться для голосования; - президентские выборы; - избирательный бюллетень; - избирательная кампания.
3. Look through all the numbers in the sentences and say if they are true or false. Give your variant if necessary: 1. American citizens under 18 may vote. 2. In 1988, at the Presidential elections, only 86 per cent of the registered voters took part in the elections. 3. There are 40 registration laws in the USA which are obligatory for the country. 4. In 1990 only 50 per cent cast their ballots. 4. Place the sentences in a right order. Try to retell the text: 1. Americans who want to vote must put down their names in a register before the election. 2. Each state can determine its own registration procedure. 3. Any American citizen, over 18 years of age has the rights to vote. 4. There is always a number of citizens who can vote but don’t. 5. There is a different registration law for each state.
5. Speak on: 1. The elections in your country.
SUPPLEMENTARY READING POLITICAL ATTITUDES It’s often been said and does seem to be true: Americans seem almost instinctively to dislike government and politicians. They especially tend to dislike “those fools in Washington” who spend their tax money and are always trying to “interfere” in their local and private concerns. Many would not doubt agree with the statement that the best government is the one that governs least. In a 1984 poll, for example, only a fourth of those asked wanted the federal government to do more to solve the country’s problems. Neighbourhoods, communities, and states have a strong pride in their ability to deal with their problems themselves, and this feeling is especially strong in the West. Americans are seldom impressed by government officials (they do like royalty, as long as it’s not theirs). They distrust people who call themselves experts. They don’t like being ordered to do anything. For example, in the Revolutionary War (1776-1783) and in the Civil War (1861-65), American soldiers often elected their own officers. In their films and fiction as well as in television series, Americans often portray corrupt politicians and incompetent officials. Anyone who wants to be the President isn’t qualified. Their newsmen and journalists and television reporters are known over the world for “not showing proper respect” to governmental leaders, whether their own or others. As thousands of foreign observers have remarked, Americans simply do not like authority. Many visitors to the US are still surprised by the strong egalitarian tendencies they meet in daily life. Americans from different walks of life, people with different educational and social backgrounds, will often start talking with one another “just as if they were all equal”. Is everybody equal in the land that stated - in the eyes of God and the law - that “all men are created equal?” No, of course not. Some have advantages of birth, wealth, or talent. Some have been to better schools. Some have skins or accents or beliefs that their neighbours don’t especially like. Yet the ideal is ever-present in a land where so many different races, language groups, cultural and religious beliefs, hopes, dreams, traditional hates and dislikes have come together. All in all, what do Americans think of their system of government? What would “We the People” decide today? One American, a Nobel Prize winner in literature, gave this opinion: “We are able to believe that our government is weak, stupid, overbearing, dishonest, and inefficient, and at the same time we are deeply convinced that it is the best government in the world, and we would like to impose it upon everyone else.” Of course, many of today’s 240 million Americans would disagree in part or with all. “Who is this one American,” they might ask, “to speak for all of us?” (2828) COURTS IN THE UNITED STATES Courts in the United States, judicial organs of government, comprising two principal systems: the federal courts, referred to as United States courts, and the state courts. The federal courts were provided for in the Constitution of the United States on the theory that the judicial power of the federal government could not be entrusted to the states, which was necessary for a strong national government. Congress passed the Judiciary Act of 1789, organizing the Supreme Court of the United States and establishing a system of federal courts of inferior jurisdiction. Federal Courts The courts established under the power granted by the U.S.Constitution are known as constitutional courts. Judges of constitutional courts are appointed for life by the President with the approval of the Senate. They are the district courts, the Courts of Appeals (before 1948, Circuit Courts of Appeals), and the Supreme Court. The Supreme Court is the highest appellate tribunal in the country and is a court of original jurisdiction in some cases. The Supreme Court is also the final judicial arbiter of federal constitutional question. Other federal courts are called 1egislative courts. These are the Claims Court, the Court of International Trade, the Tax Court, and the territorial courts established in the federally administered territories of the United States. State Courts Each state has an independent system of courts operating under the constitution and laws of the state. The character and names of the courts differ from state to state. The state courts as a whole have general jurisdiction, except in cases in which exclusive jurisdiction has been vested in the federal courts. (1680)
COST OF GOVERNMENT The average cost of all governments- federal, state, and local- to each man, woman and child in the United States is 4539$ a year. About two-thirds of all taxes collected go to the federal government. The individual income tax provides the federal government slightly less than half its revenues. A person with an average income pays about 11 per cent of it to the government; those with very large incomes must pay up to 50 per cent. Many states also have their own income taxes. Many other taxes- on property, entertainments, automobiles, etc. - are levied to provide funds for national, state and local governments. Federal government spending for defence purposes, including military help to other nations, has fallen as a portion of total government expenditures from 58.7 per cent in 1958 to 25.7 per cent in fiscal year 1981. The remaining 74.3 per cent of the federal budget has gone into public welfare programmes, development of water and land resources, public health and education. As a result of the expansion and increased costs of government services, the national debt has increased greatly since World War II. (1124) THE LAWMAKING PROCESS One of the major characteristics of the Congress is the dominant role committees play in its proceedings. Committees have assumed their present-day importance by evolution, not by constitutional design, since the Constitution makes no provision for their establishment. At present the Senate has 16 standing (or permanent) committees; the House of Representatives has 22. Each specializes in specific areas of legislation: foreign affairs, defense, banking, agriculture, commerce, appropriations and other fields. Every bill introduced in each house is referred to a committee for study and recommendation. The committee may approve, revise, kill or ignore any measure referred to it. It is nearly impossible for a bill to reach the House or Senate floor without first winning committee approval. In the House, a petition to discharge a bill from committee requires the signatures of 218 members; in the Senate, a majority of all members is required. In practice, such discharge motions only rarely receive the required support. The majority party in each house controls the committee process. Committee chairmen are selected by a caucus of party members or specially designated groups of members. Minority parties are proportionally represented on the committees according to their strength in each house. Bills are introduced by a variety of methods. Some are drawn up by standing committees; some by special committees created to deal with specific legislative issues: and some may be suggested by the president or other executive officers. Citizens and organizations outside the Congress may suggest legislation to members, and individual members themselves may initiate bills. After introduction, bills are sent to designated committees which, in most cases, schedule a series of public hearings to permit presentation of views by persons who support or oppose the legislation. The hearing process, which can last several weeks or months, opens the legislative process to public participation. (2009) ELECTIONS The US Constitution includes some general provisions on the franchise. It sets forth certain requirements for candidates running for a post of a president, vice-president, senator or member of the House of Representatives. Requirements usually concern age, residence and citizenship. The candidates who meet all these requirements are considered eligible for office. A residence qualification requires a permanent residence of an individual in order to get the right to vote. The duration of the residence qualification is, in general, a few months though it may substantially vary from state to state. Besides, some states have the so-called literacy qualification (the voter should be able to read and speak English, he (she) must know how to interpret the US Constitution, etc. And at last it should be mentioned that in some states a poll tax is levied upon everyone who votes and this certainly discourages poor citizens and Negroes from voting. In this context, it is not surprising that not all the Americans participate in elections, including congressional or presidential elections. The voters are registered by clerks of counties or towns and by local election commissions. When registering, the voter must produce an identification card. This is done to prevent fraud. The administration of elections is vested in an election commission which ordinarily is composed of two commissioners, one representing each of the major parties, and a third ex officio member, usually a sheriff, a county judge, or a clerk. Prior to holding primary or general election, the commission appoints election officers for each precinct and also arranges for polling places. After the ballots have been cast, they are counted and the results obtained are tabulated and returned to the election commission. (1862)
БИБЛИОГРАФИЧЕСКИЙ СПИСОК Kirn E., About the USA. Delta System, 1989 – 68 p. Longman Advanced American Dictionary. Longman, 2000. Macmillan English Dictionary for Advanced Learners. International Student Edition. London, 2002. Short D. et al., By the People, for the People. U.S. Government and Citizenship., Delta System, 1999- 32 p. Гуманова Ю.Л. и др. Just English. Английский для юристов. Под ред. Т.Н. Шишкиной. - М.:1998- 78 с. Американа. Англо-русский лингвострановедческий словарь // Г.В. Чернов и др. М., 1996.
____________________________________________________________ Лицензия РБ на издательскую деятельность № 0261 от 10 апреля 1998 года. Подписано в печать __.__.2010 г. Формат 60х84/16. Бумага типографская. Гарнитура Таймс. Усл. печ. л. ___. Усл. изд. л. ___. Тираж ___экз. Заказ № ___. Издательство Башкирского государственного аграрного университета. Типография Башкирского государственного аграрного университета. Адрес издательства и типографии: 450001, г. Уфа, ул. 50 лет Октября, 34
UNIT I I. US GOVERNMENT 1. Read and translate the text: The USA is a presidential republic. The legislative branch of the US Government, or the Congress, represents all of the American states. It consists of two parts: the House of Representatives and the Senate. Each state has two senators, who are elected every 6 years. The job of the Congress is to make laws. The President can veto a bill. The Congress can pass the law anyway if it gets a two-thirds majority vote. The Congress can also declare war. The House of Representatives can also impeach the President. This means that the house can charge the President with a crime. In this case, the Senate will put the President on trial. The Senate votes to approve the justices that the President appoints to the Supreme Court. The executive branch of the government puts the country laws into effect. The President of the United States is a member of the executive branch. The President is elected every four years and cannot serve more than two terms. The Vice-President of the USA is a president of the Senate. When the President receives a bill from the Congress, he must sign it, and then the bill becomes a law. However if he disagrees with the law, he can veto it. The President can also ask the Congress to declare war. He also appoints the justices to the Supreme Court. He must do his job according to the Constitution, or he may be impeached. The judicial branch of the government is the system of courts in the United States. Its job is to enforce laws. The Supreme Court is the highest court in the country. It consists of 9 justices: one Chief Justice and 8 Associate Justices. The President appoints justices but the Senate must approve them. The judicial branch works together with the legislative and executive branches to protect the Constitution and the rights of people. Vocabulary: the House of Representatives- Палата представителей the Senate- Сенат to impeach the President- подвергнуть президента импичменту to charge- обвинить в каком-либо преступлении a term- срок полномочий the Supreme Court- Верховный Суд Chief Justice- Главный Судья Associate Justice- Член Верховного Суда
2. Make up your own sentences with the following verbs. You may use the text: to elect; to appoint; to sign; to consist; to become; to vote.
3. Finish the sentences according to the text: 1. The job of the Congress is…………………………………………. 2. The President appoints…………………………………………….. 3. The Senate votes.…………………………………………………... 4. The Supreme Court is……………………………………………… 5. The Supreme Court consists of…………………………………..... 6. The judicial branch is………………………………………………
4. Find the English equivalents for: - представлять; - накладывать вето на законопроект; - приводить в действие; - объявить войну; - привлечь к суду (судебному разбирательству); - проводить закон в жизнь; - назначать.
5. Answer the questions: 1. What branches does the government of the USA consist of? 2. Who does the highest executive power belong to? 3. Who represents the legislative power in the USA? 4. What is the judicial branch of the government? What is its job? 5. What can you say about the Supreme Court of the USA?
6. Speak on: 1. The government in your country.
II. EXECUTIVE BRANCH: PRESIDENT, VICE-PRESIDENT AND THE CABINET
1. Read and translate the text: The executive branch, which includes the President, the Vice-President and the Cabinet consisting of Secretaries of the executive departments, is responsible for administering and executing the laws.
If the President dies, or resigns, or can’t work, the Vice-President becomes the President. So the qualifications for the Vice-President are the same as for the President. Within the Executive Branch, there are 14 executive departments. These are: the Departments of State, Treasury, Defense, Justice, Interior, Agriculture, Commerce, Labour, Health and Human Services, Housing and Urban Development, Transportation, Education, Energy, and Veteran Affairs. Each department is established by law and is responsible for a specific area. The heads of the executive departments are Cabinet members, they are appointed by the President. These appointments, however, must be approved by the Senate. All the Secretaries of the executive departments make up the Cabinet and are Presidential assistants and advisors.
Vocabulary notes:
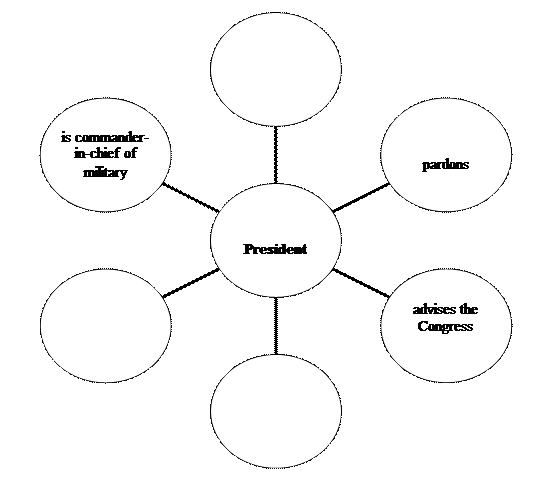
1. Complete the scheme below according to the information given above and try to retell the text. Duties of the President and Vice-President
2. Find the English equivalents for: - Главнокомандующий вооруженными силами; - вести внешнюю политику; - утверждать закон; - амнистировать; - назначение.
3. Answer the following questions: 1. Who does the Executive branch include? 2. How many executive departments are there in the Cabinet? 3. Who appoints or elects the heads of the executive departments? 4. What qualifications should a person have to be elected the President of the USA? 5. How often is the President elected? 6. What are the functions of the President? 7. Why do the Americans have a Vice-President?
4.Choose the correct answer: The President… 1. makes plans for foreign policy 2. appoints people to the Supreme Court 3. writes taxes for states 4. votes in the Senate 5. sends soldiers to a war The Vice-President… 1. vetoes laws 2. votes in the Senate 3. acts as a President 4. pardons 5. is the President of the Senate
5. Read the text without a dictionary and be ready to introduce each department:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-08-16; просмотров: 100; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.220.1.239 (0.438 с.) |
 The President of the United States is elected every four years to a four-year term of office, with no more than two full terms allowed. The President is elected directly by the voters (through state electors). He must be a native-born citizen at least 35 years old and live in the U.S. for not less than 14 years. The President is the head of the state and the government, and the Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces. He makes foreign policy, approves or vetoes laws, appoints judges, advisors and ambassadors, he can pardon a person for a federal crime (give amnesty).
The President of the United States is elected every four years to a four-year term of office, with no more than two full terms allowed. The President is elected directly by the voters (through state electors). He must be a native-born citizen at least 35 years old and live in the U.S. for not less than 14 years. The President is the head of the state and the government, and the Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces. He makes foreign policy, approves or vetoes laws, appoints judges, advisors and ambassadors, he can pardon a person for a federal crime (give amnesty).


 We can follow any religion: we can say our thoughts, write articles in newspapers, meet in groups.
We can follow any religion: we can say our thoughts, write articles in newspapers, meet in groups. The question is about who should be the new President began to divide people into political organizations. On one hand there were the Federalists, representing business, finance and the middle classes of city folk. On the other hand there were the “Republicans” led by Thomas Jefferson. They represented mainly the country folk from Virginia. Thus by 1800 the one-party Revolutionary government of the United States quickly split up into a two-party system.
The question is about who should be the new President began to divide people into political organizations. On one hand there were the Federalists, representing business, finance and the middle classes of city folk. On the other hand there were the “Republicans” led by Thomas Jefferson. They represented mainly the country folk from Virginia. Thus by 1800 the one-party Revolutionary government of the United States quickly split up into a two-party system. Democrats often want the government to establish social programs for people in need, such as the poor, the unemployed, and the elderly. They usually say they believe in equal rights for women and minorities and they oppose nuclear weapon and too much military spending. The symbol of the Democratic Party is the donkey.
Democrats often want the government to establish social programs for people in need, such as the poor, the unemployed, and the elderly. They usually say they believe in equal rights for women and minorities and they oppose nuclear weapon and too much military spending. The symbol of the Democratic Party is the donkey.