
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
The description of the geographical position of the continent
1. Geographical position(equator, tropics, Greenwich meridian) 2. Extreme points of the continent 3. Oceans, seas, gulfs, bays around the continent 4. Peninsulas, inlands near the continent 5. Climatic belts 6. The nearest continents 7. Who explored the continent
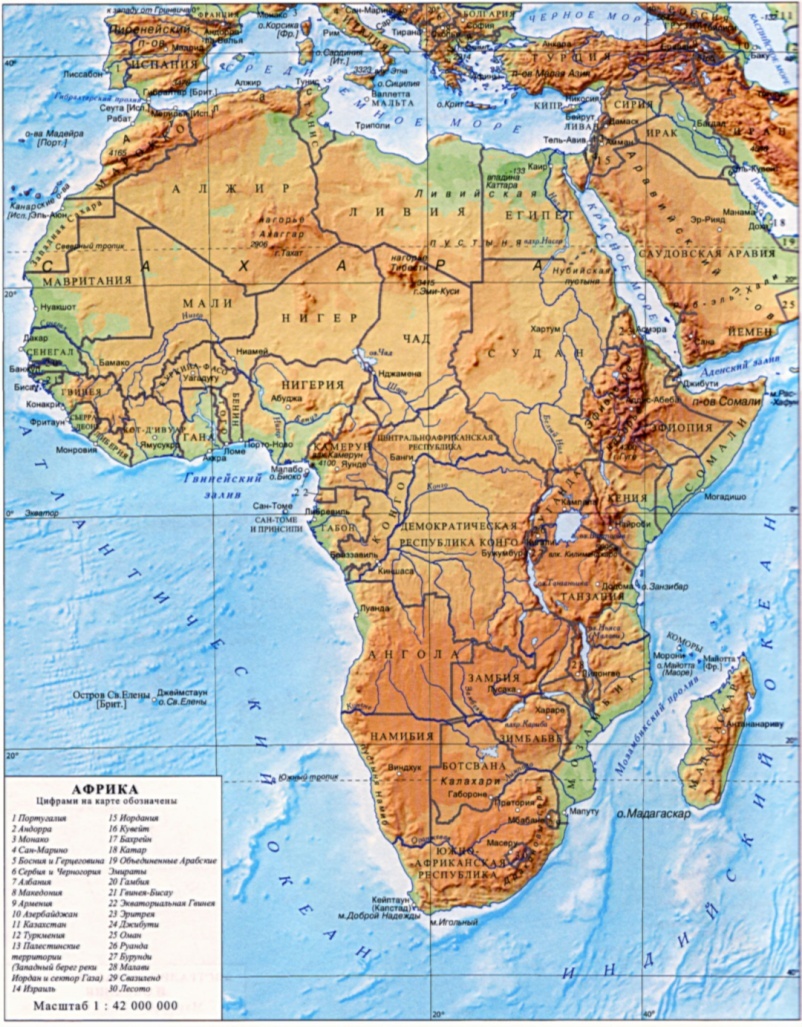
1.Geographical Position. Africa is divided by the equator almost in the middle and lies in the northern and southern hemispheres between the tropic of Cancer and the tropic of Capricorn in the Torrid Zone. It is rather a big continent. The total area of Africa is 30.3 million sq km. The average height over the sea level is 750 m. There are four extreme points in Africa: North – cape El-Abyard; South – cape Igolny; East – cape Hafun; West – cape Almadi. Africa is washed by the Atlantic Ocean in the west, by the Indian Ocean in the east, by the Mediterranean Sea in the north and by the Red Sea in the north - east. The Strait of Gibraltar separates it from Europe and the Sues Canal (160 km long) – from Asia. The coastlines are unbroken: there is only one big peninsula – Somaliland, and only one big gulf – the Gulf of Guinea. The total length of the coastlines without islands is 30.5 thousand km. The largest island near Africa is Madagascar.
Long ago Africa attracted the attention of people from Europe and Asia. The first were ancient Greeks who tried to explore the continent and settled on the northern coasts of it. Ancient Egyptians also explored Africa and reached Somaliland, but they couldn’t enter the central part of the continent because of the deserts.
In the middle of the 19-th century the English traveler David Livingstone (1813 - 1873) explored the Zambezi River. He discovered the great waterfall called Victoria. He described his trips to the Congo River, Lake Nyasa and others. He wanted to find the source of the Nile but he died of an unknown tropical disease. Almost at the end of the 19-th century an American journalist Henry Stanley (1842 – 1904) came to Africa. He swam along the river Congo three years and watched the flow of it. Then he explored Lake Victoria and found the beginning of the Nile. He also explored Lake Tanganyika and some cavities on the River Congo. One of the Russian explorers of Africa was Vasily Younker (1840 - 1892). He travelled to the central and eastern parts of the continent in the second half of the 19-th century. He explored the Nile and the Congo and found a lot of interesting facts about the nature and the life of people in these parts of the continent.
Task: Complete the table.
3.Relief. The relief of the continent is not complicated. We can find only mountain ranges and highlands there. There are the Atlas Mountains in the north-west of the continent and the Drakensberg Mountains in the south - east of it. In the middle of the continent, there are the Abyssinian Highlands and the East-African Highlands. The highest mountain in Africa is an active volcano - Kilimanjaro (5 876 m.). There are four deserts in Africa: the Sahara Desert, the Libyan Desert, the Namib Desert and the Kalahari Desert. Africa is rich in minerals. It has vast deposits of iron ore, copper, tin, uranium, gold and diamonds {minerals of igneous origin). Minerals of sedimentary origin are oil, gas, coal, salt, manganese and phosphorites.
4.Climate. Africa lies within the zone, where the sun is high above the horizon throughout the year. That is why Africa’s average temperature is above 20oC. The extreme north and south are the coolest parts having a subtropical climate. The circulation of atmosphere influences the rainfalls. Equatorial regions get many rains. In the north and south, there are little rains because the belts of high atmospheric pressure are situated there. Temperate air masses and western winds bring rains to those regions in winter. Summer is dry because tropical air masses and trade winds influence it. Trade winds predominate in Africa. The relief also influences the climate greatly. Climatic belts Since the equator crosses Africa in the middle all the climatic belts, but the equatorial are met twice. The equatorial climatic belt is situated in the Congo basin and the coast of the Gulf of Guinea. The equatorial air masses make the climate hot and wet. It is a region of low pressure and the temperature are about +24,+28C all year round. The sky is usually clear in the morning. By midday it is covered with clouds and then comes a heavy downpour often followed by a thunder shower. By the evening the sky is clear again. North and south of the equator extend subequatorial climatic belts. The t* is high, but nearly all the rain falls in summer. So these regions have 2 distinct climatic periods: a wet period in summer and a dry period in winter. North and south of the subequatorial climatic belts extend 2 tropical belts. The dry tropical air masses and trade winds blow there. The part of Africa lying in the northern hemisphere stretches the vast Sahara desert. The ground becomes very hot in the daytime; the t*in summer sometimes reaches 50-60*C in the shade. At night, on the other hand, it is cold. In the south deserts occupy a smaller area, as the continent is much narrower there. The Namib Desert and the Kalahari Desert are situated there. The tropical wet climate is in the eastern regions of the island Madagascar and the Drakenberg Mountains. Along the shores of the Mediterranean Sea to the north of Africa and in the extreme south the climate is subtropical. In the north there is the Mediterranean climate with hot and dry summer and mild and wet winter. In the south there is the subtropical climate where the rain falls all year round, but mostly in summer.
Climatic Belts. (Laboratory Work.)
5.Inland Waters.
The Nile is the biggest river in the world. It begins in the mountains of East Africa, flows north and falls into the Mediterranean Sea. The second largest river in Africa is the Congo. It begins in the East-African Highlands, flows west and falls into the Atlantic Ocean. The waters of the Niger flow into the Gulf of Guinea. The river rises in the mountains and has many waterfalls. The Zambezi River flows east and falls into the Indian Ocean. It forms a great waterfall called the Victoria Falls. The lakes are situated in the centre of the continent. The deepest is Lake Tanganyika (1 435 m). It is 650 km long and 80 km wide. The largest in area is Lake Victoria (80 m deep). In the south of the Sahara Desert, there is Lake Chad (4-7 m deep).It is not deep, but often changes its shape, depending on the amount of rain. There are two more lakes: Lake Nyasa (706 m deep) and Lake Aswan.
6.Natural Zones
Vast territories of the dry land with similar natural complexes are formed under the influence of the combination of warmth and moisture is called natural zones.
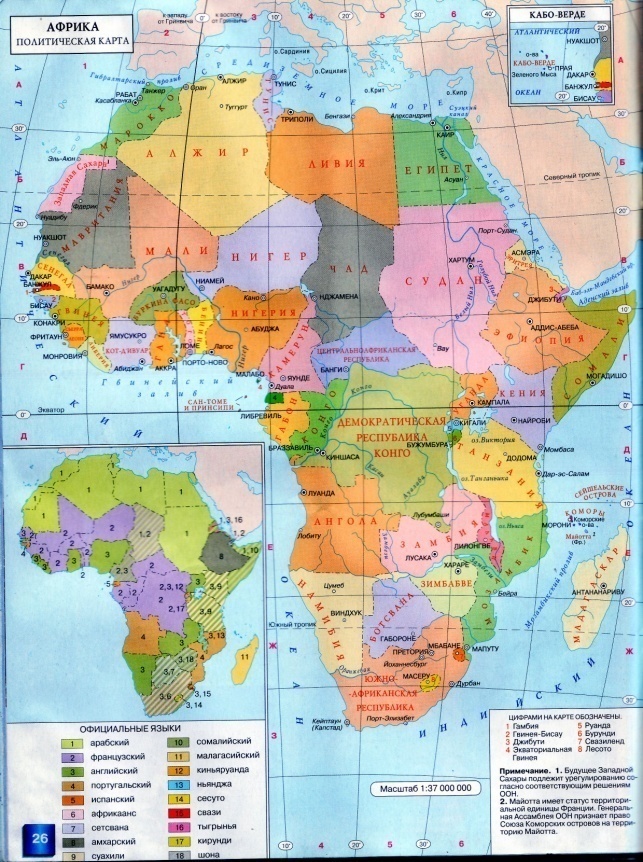
7.Population of Africa. Within Africa live over 600 million people. The average density of population is eight people to the square km. Most densely populated are the lands of the Nile Valley. Some regions in deserts are very thinly populated or unpopulated at all. Population of Africa today consists of native peoples and the settlers from Europe. It belongs to 3 races: europeoid, equatorial and mongoloid. There live - the Arabs(who live mostly in Egypt and north Africa) - the Negroes(who live in the west Africa and Sudan) -the Bushmen (who occupy the Kalahari Desert, the Pygmies-the Congo river and the Hottentots- of the south –west of Africa) -The Hamites (occupy Ethiopia and much of the Sahara Desert) -The Bantus, negro people (occupy much of central and southern Africa) There are also about five million white people in Africa. Most of them live along the north coasts of Africa and in the southern regions. There are many countries in Africa.
Plan to describe the country: 1. Geographical position. Capital. 2. Social system. Peoples. 3. Climate. 4. Animal life and vegetation. 5. Rivers and lakes. 6. Some interesting facts. Places of interest.
Home task: choose any country from the list and make up a report according to the
Tanzania is a country in the east of Africa. Its official name is the United Republic of Tanzania. The capital of the country is Dodoma. The total area of the country is more than 900 000 sq km (945 087 sq km). It borders on Kenya and Uganda in the north, on Mozambique, Malawi and Zambia in the south, on Congo, Burundi and Rwanda in the west. It is washed by the Indian Ocean in the east and has some islands in its waters.
The climate of Tanzania changes with the height over the sea level. On the coastlines, the climate is tropical, where the temperature is +27 o C all year round. Deep in the continent, it is warmer and drier. The rainfalls season lasts from December until May here. Many rainfalls are on the western coasts of Lake Victoria (over 2000 mm a year).
There are many places of interest in Tanzania. Among them is the National Museum in Dar es Salaam, the fortress ruins, picturesque caves Ambony and others. Many tourists visit safari parks and Kilimanjaro.
Australia. 1. Geographical Position.
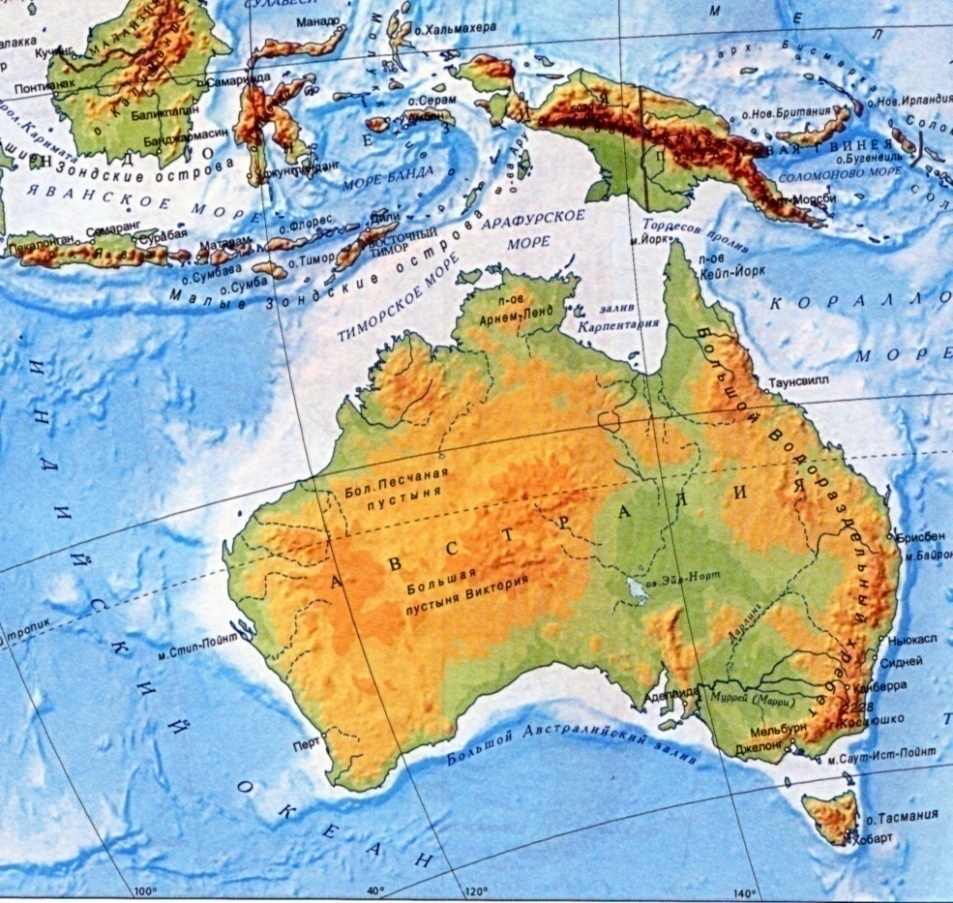
Australia is the smallest continent in the world. Sometimes it is also called the biggest island. The total area of Australia is 9 million sq km. It lies wholly within the southern hemisphere and has only one country with the same name. There four extreme points in Australia:
North – cape York; South – cape South –Eastern; West – cape Steep Point; East – cape Byron. Australia is washed by the Indian Ocean in the west, by the Pacific Ocean in the south - east, by the Coral Sea in the north - east, by the Arafura Sea in the north and by the Tasmanian Sea in the south. The coastlines of the continent are rather smooth with few peninsulas and bays. They are: the Cape York peninsula, the Arnhem Land peninsula and the Gulf of Carpentaria in the north; the Great Australian Bight in the south. The length of the coastlines without islands is 19.7 thousand km. Near Australia we can find some big islands as Tasmania, New Guinea and New Zealand. The closest continent is Eurasia. Along the eastern coast of Australia there is the Great Barrier Reef, which extends for 2000 km and is built by the coral polyp.
2.The Discovery of Australia. Australia lies far from the other continents. For this reason, people didn’t know about it for a long time. At the beginning of the 17-th century Australia was discovered by the Dutch. In 1643 the Dutch sailor Abel Tasman (1603 - 1659) reached the unknown island. Later the island was called after him. He also discovered the western coasts of New Zealand and a lot of small islands in the Pacific Ocean. Tasman proved, that Australia was a separate continent.
Task: Complete the table.
3. Relief. Australia is a low continent consisting mainly of plains and lowlands. The average height over the sea level is 215 m. There are only two mountain ranges there: the Great Dividing Range Mountains in the east and the Australian Alps in the west. There is one big plain in Australia - the Central Lowland. We can also find two deserts there – the Great Victoria Desert and the Great Sand Desert.
4.Climate. Australia lies close to the equator in the north and southern part of Tasmania lies within temperate zone. Most of the continent is influenced by trade winds. In the north monsoons blowing from the Indian Ocean, cause heavy rains. The extreme south-west and south receive rain mainly in winter when western winds are blowing from the Indian Ocean. In summer the temperature is very high in Australia. In winter the continent is cool. High in the mountains there is frost and snow in winter. All in all it is usually rather dry during the year. Climatic Belts. In the north of the continent the climate is subequatorial. In the centre there are 2 types of tropical climate: tropical dry in the west and centre and tropical wet in the east. In the south there are 3 types of subtropical climate: Mediterranean subtropical wet and subtropical continental. Island of Tasmania lies in temperate climatic belt.
(Laboratory Work).
5. Inland Waters. Australia is rather a dry continent. There are not many rivers and lakes in Australia, many of which are drying. The biggest rivers are the Murray (2 570 km) and its tributary the Darling (2 740 km). They begin in the Great Dividing Range and flow into the Indian Ocean. There are some lakes: the Eyre, the Mc Kai, the Carnegie, the Herdner and the Torrens. They are situated in the central and western parts of the continent but have salty water. The largest lake is Lake Eyre. It is fed by creeks that bring much water after downpours. In the dry season the lake grows shallow again and divided into pools.
The central arid part of Australia is very rich in underground water. Deep artesian wells are situated here. This water is salty that is why is used only in industry and agriculture.
6. Natural Zones.
7. Population. Australia is the least populated continent. Over 19 million 400 thousand people live here. The average density of population is a little over one person to the square km. the greater part of the inhabitants live in the east, south-east and south-west of the continent. All large cities are situated here. North and west are almost unpopulated. There is only one country on the continent. Its official name is the Commonwealth of Australia. Its capital is Canberra. The biggest cities are Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Hobart, Perth, Adelaide and others.
Answer the questions:
1. In what hemisphere does Australia lie? 2. What oceans is Australia washed by? 3. Can you name the extreme points of the continent? 4. Do you know the islands which lie near the continent? 5. Are the coastlines broken or unbroken and smooth? 6. Who discovered Australia? 7. Are there rivers and lakes on the continent? Name them. 8. What rivers flow into the Indian Ocean? 9. What is the population in Australia? 10. What are the peculiarities of vegetable and animal life in Australia?
Antarctica.
1.Geographical Position. Discovery. Antarctica lies wholly within the Antarctic Polar Circle. It is the only continent in the Earth covered with ice all over. The total area of the continent is 14 million sq km. The average height over the sea level is 580 m. The length of the coastlines is 30 thousand km. Antarctica is the most isolated continent surrounded by the oceanic water on all sides. The Atlantic, the Pacific and the Indian Oceans wash Antarctica. The seas around Antarctica are: the Weddell Sea, the Bellingshausen Sea, the Amundsen Sea and the Ross Sea. The nearest continent is South America. Antarctica was discovered only at the beginning of the 19th century. The honour of discovery fell on a Russian expedition under the command of Fadei Bellingshausen (1778 – 1852) and Michael Lazarev (1788-1851). During a voyage lasting from 1819 to 1821 they rounded the continent on two vessels and several times approached the shore. They also discovered some islands gave them Russian names. The South Pole was reached in 1911 by the Norwegian explorer Rual Amundsen (1872 - 1928) and by the English explorer Robert Scott (1868-1912) a month later. The expedition under the command of Amundsen was well - prepared. Their trip lasted 99 days. They used dogs as a kind of transportation and returned to Norway safe and sound. As for Scott, he and his people decided to use another road. They went to the pole using ponies, but the animals couldn’t stand the severe frost of the continent and died. Because of that, people had to pull 300-kilo sledges themselves and were late for a month. They were exhausted, had almost nothing to eat and died on the way back.
John Weddell (1787-1834) was an English explorer, who went along the coastlines of Antarctica and discovered the sea in 1823. Later it was given his name. Another English explorer was James Ross (1800-1862). In 1840 he discovered a new see, which was called after him. He also explained the existence of the ice range on the continent.
Antarctica doesn’t belong to any state. On October 15, 1959, 12 countries signed an agreement, which made Antarctica neutral territory designed for scientific research only. Nowadays 38 countries are committed to this agreement. There are 140 stations here, 20 of which are Russian. It is interesting to mention that Russian stations are situated in the most severe parts of the continent.
Antarctica is the coldest continent in the world. It is the kingdom of permanent frost. The climate here is very severe. The to in winter is -70oC, in summer -30oC. The high atmospheric pressure belt forms the antarctic air masses, which are very cold and dry. The antarctic climatic belt is situated here. On the coastlines and near-by islands the to in summer is 0o + 10oC, in winter -16o-32oC. They lie in the antarctic climatic belt.
3.Natural Resources. Antarctica is situated in the antarctic desert zone. The vegetation and the animal life are poor here. Life exists mainly on the coasts and islands. In summer, there are seaweeds, moss and lichen. The seas are rich in plankton and fish. Seals, sea elephants, fur seals and whales live there. The birds as gulls, cormorants, petrels and albatrosses make their nests on the rocks in summer. There are also 17 kinds of penguins in Antarctica. Antarctic Penguins, Subantarctic Penguins, Adele Penguins and King Penguins are among them.
Home task: make a short report on some interesting facts about Antarctica.
Answer the questions:
1.Where does Antarctica lie? 2. Who discovered Antarctica? 3. What can you say about the climate of Antarctica? 4.Why the vegetation and the animal life is poor?
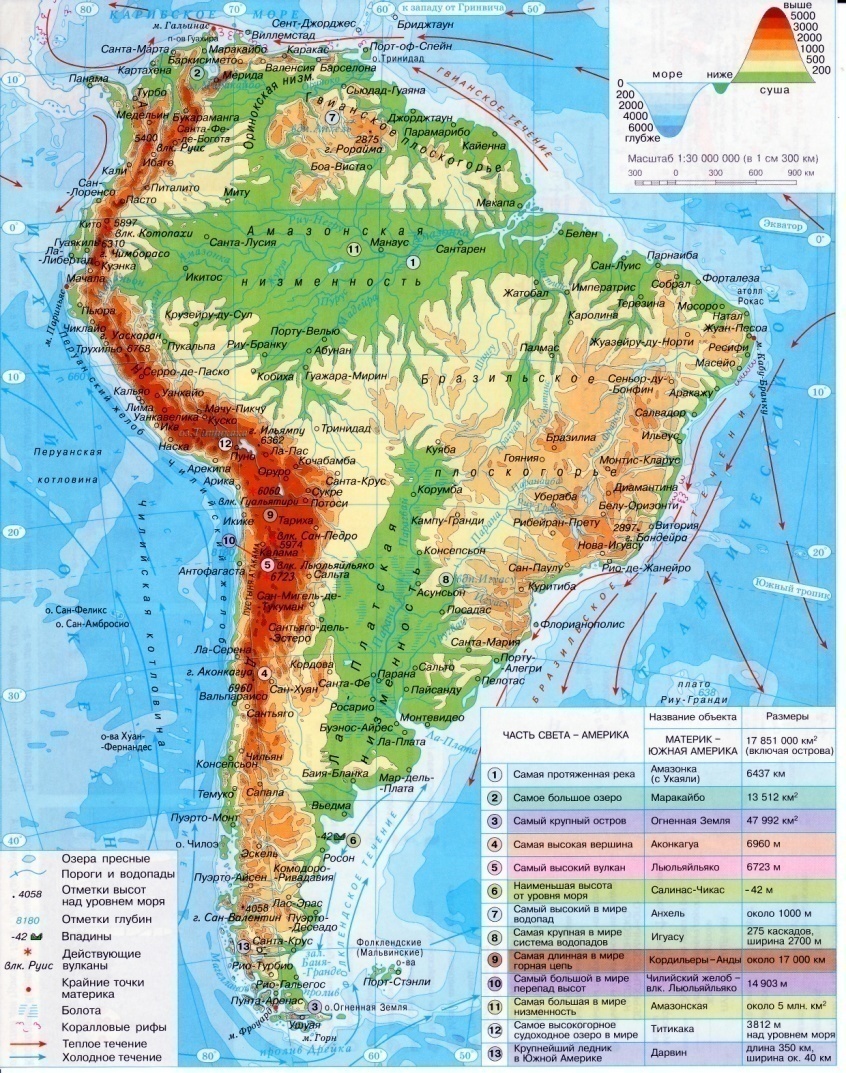
South America. 1.Geographical Position. America consists of two continents South America and North America. These two continents are separated from each other by the Panama Canal. The total area of South America is about 18 (17.8) million sq km. The continent is crossed by the equator in the north. It is washed by the Caribbean Sea in the north, by the Atlantic Ocean in the east and by the Pacific Ocean in the west. The extreme points of the continent are: North – cape Gallinas; South – cape Froward; East – cape Kabu-Branku; West – cape Parinas. South America has a form of triangle. The coastlines are unbroken, because there is not a single large peninsula or deep bay. The length of it without islands is 26 thousand km. In the south -east there is the La Plata Bay. The Strait of Magellan separates the island Tierra del Fuego from the continent.
A lot of expeditions visited the New World later. But it was called America only when another explorer from Spain Amerigo Vespucci (1454 – 1512) described it as a new part of the world. He was the first to think about it and to prove it, exploring the land. After that a lot of people went to America to live there and explore the continent. They were mostly from Europe. One of them was Alexander Humboldt (1769 – 1859) a German sailor, who explored the northern coastline of South America. Together with the French biologist Emi Bonplan he went deep into the continent. There they discovered the Orinoco River. At the beginning of the 19-th century the German sailor Gregory Langsdorf (1774 – 1852) became a leader of the Russian expedition to America. He studied nature and native people of the continent. During his travelling he made a lot of discoveries at the Brazilian Highlands.
Task: Complete the table.
3.Relief. South America lies on the South American platform, that is why it is rather a low continent. The average height over the sea level is 580 m. There are many plains on the continent. The largest plain in the world – the Amazon Lowland – is situated in the north of the continent close to the equator. To the north from it, there is the Orinoco Lowland, to the south – the La Plata Lowland. In the eastern part of the continent, there are the Brazilian Highlands. Further north are the Guiana Highlands. Along the western coast a large mountain range called the Andes lies. The volcanic activity goes on in the Andes today. The highest volcanoes are Chimborazo (6 310 m) and Cotopaxi (5 896 m). The highest mountain of the Andes is Aconcagua (6 960 m). South America is rich in copper, tin, lead, zinc, precious stones, iron ore, uranium, gold, aluminum.
4.Climate. South America is crossed by the equator in the north and lies in the equatorial, subequatorial, tropical, subtropical and temperate climatic belts. The continent is not as dry as Australia and not so hot as Africa. It is influenced by the trade winds from the Atlantic Ocean. These winds usually bring heavy rains. Along the western coasts runs the cold Peruvian current, which cools the air and prevents the rains. The east coast is sheltered from the western winds by the Andes and is dry. The temperate continental clime is formed here. Warm summer, cold winter and a little sum of rains (200-300 mm a year) are often here. In the mountains the climate is cooler the in the plain. The Andes have an alpine climate which changes with the altitude and is very varied near the equator. At the foot the Andes the climate is wet and warm. The equatorial climatic belt is situated here, but the top of Cotopaxi is covered with snow all year round.
Climatic Belts. (Laboratory Work).
5. Inland Waters.
The greatest river is the Amazon (6 400 km). It rises in the Andes, flows across the Amazon Lowland into the Atlantic Ocean. It has 500 tributaries. Among them, we can find the Madeira, the Riu-Negru, the Maranion, the Jurua, the Purus. The second largest river is the Parana (4 700 km). It rises in the Brazilian Highlands, flows across the La Plata Lowland into the Atlantic Ocean. It has some tributaries: the Paraguay, the Uruguay, the Iguassu (the Iguassu Waterfalls). Across the north of the continent flows the Orinoco (2 740 km). It rises in the Guiana Highlands and flows into the Atlantic Ocean. It has a lot of rapids and high waterfalls. The Anhel Waterfalls are also here. The tributaries of the river are the Caroni, the Meta, the Apure and others. The lakes of South America are not numerous. The deepest lake is Titicaca (304 m deep). It lies in the middle part of the Andes. In the north of the continent, there is another big lake – Lake Maracaibo (250 m deep).
6. Natural Zones.
7.Population. The greater part of the present day population of South America are descendants of settlers from different countries of Europe. More than 330 million people live in South America. The average density of population on the Atlantic coast is 50 -100 persons to the sq km. There are many countries in South America.
Home task: choose any country and make a report according to the plan (see page 18).
The republic of Ecuador is a country on the northeastern coasts of South America. The name of it comes from Spanish phrase meaning “on both sides of the equator”. The total area of it is nearly 300 000 sq km (272 045 sq km). It borders on Columbia in the north and on Peru in the east and south. It is washed by the Pacific Ocean in the west. The capital of the country is Quito. The country is ruled by the parliament. The head of the state is the president. It is divided into 22 provinces. The state language is Spanish. Different peoples live on the territory of Ecuador. The population of the country is 13 million 184 thousand people. The climate of the country is equatorial, and in some southern parts, it is subequatorial. The temperature here is +23 o C +27 o C. It is mostly hot and wet.
There are some places of interest in Ecuador. They are mostly in Quito. The Archeological Museum, St Francisco Church, St Augustine Church and the Parliament Palace are among them.
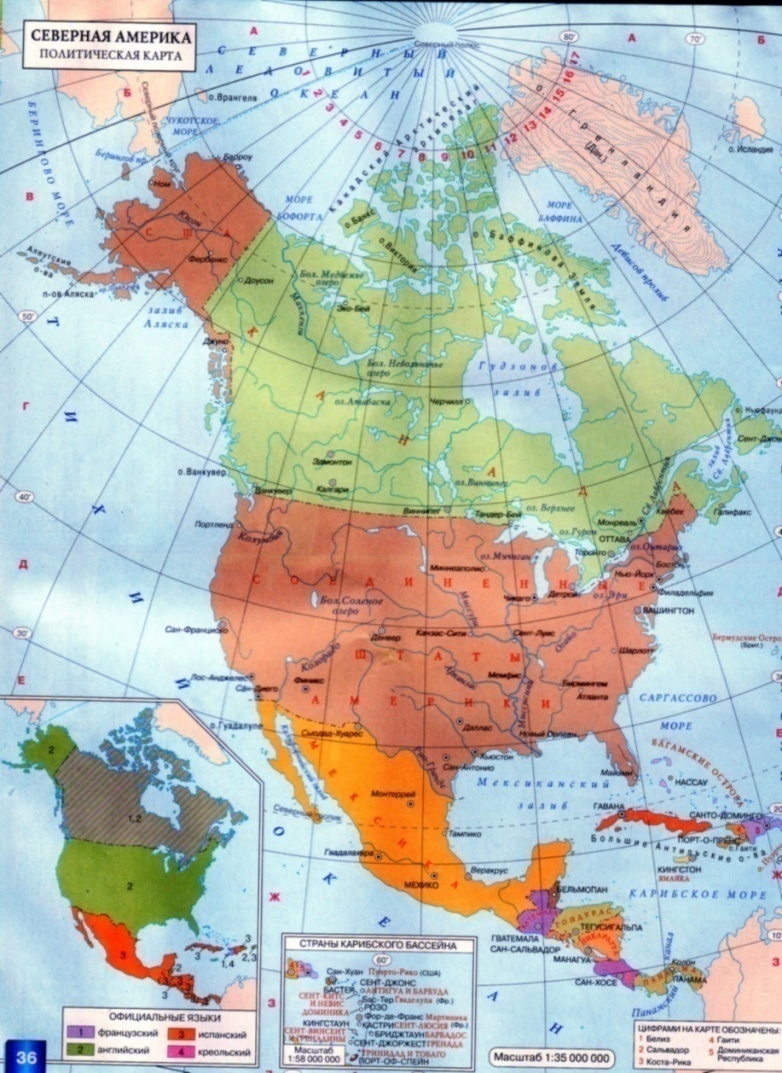
North America. 1.Geographical Position. North America lies in the western hemisphere. It is washed by the Pacific Ocean in the west, by the Atlantic Ocean in the east and by the Arctic Ocean in the north. It is washed by the Caribbean Sea in the south, by the Sargasso Sea in the south – east, by the Baffin Sea in the north and by the Bering Sea in the north – west. The total area of the continent is 24.2 million sq km. It is not crossed by the equator, but comes close to it. The Bering Strait separates North America from Eurasia and the Panama Canal - from South America. The extreme points of the continent are: North – cape Murchison; South – cape Mariato; West – cape Prince of Wales; East – cape Saint Charles. The coastlines are broken in the north and in the east. The length without islands is 60 thousand km. There are some large peninsulas in North America: Alaska, Florida, California, Labrador and Yucatan. There are also three big gulfs: the Gulf of Mexico and the Californian Bay in the south, the Hudson Bay in the north. Numerous islands surround the continent. The Aleutian Islands, The Baffin Island, the Island of Victoria, Newfoundland, the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, Greenland, Cuba, Jamaica, the Haiti Island, the Hawaii. North America also has the greatest island archipelago in the world – the Canadian Arctic Archipelago.
The European sailors reached the coasts of Greenland and the northeastern coasts of North America as far back as the 10-th century. They were the Normans. After that a lot of people came to the continent to explore it.
A lot of great discoveries were made during the period of 400 years. A lot of sailors and explorers came to study an unknown continent. Among them was Henry Hudson (1550 – 1611) an English sailor, who was looking for a pass from the Atlantic Ocean into the Pacific one. While travelling along the continent he discovered a river, a strait and a bay. They all were called after him (the Hudson Bay, the Strait of Hudson, the Hudson River). Another English sailor and explorer was William Baffin (1584 – 1622). He explored the northern polar circle, the Hudson Bay and some seas to the west from Greenland. He discovered many islands of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago and the sea called after him the Baffin Sea. A Scottish merchant Alexander Mackenzie (1764 - 1820) explored the Great Slave Lake. While travelling there, he discovered a river, a lowland and a bay, that later were called after him (the Mackenzie River, the Mackenzie Lowland and the Mackenzie Bay). He travelled across North America twice. A famous English scientist James Ross (1800 - 1862) was very much interested in the North Pole. In 1831 he discovered the northern magnetic belt and pole. He also explored the islands and the northern coasts of North America. Among his discoveries there is a sea called after him – the Ross Sea. Arctic has always interested Russian people. A famous Russian sailor Vitas Bering (1681 – 1741) found the pass between the Chukot Peninsula and the Alaska Peninsular and went into the Pacific Ocean. The strait and the sea in the Pacific Ocean got their names after him. He also discovered some of the Aleutian Islands. Another Russian sailor was Alexei Chirikov (1703 – 1748). He discovered some parts of the coasts of North America and some of the Aleutian Islands.
Task: Complete the table.
3.Relief. The relief of the continent is not very complicated but rather varied. There are mountains, plains and lowlands. The average height over the sea level is 720 m. Along the western coast of the continent there are high mountains called the Cordilleras. They consist of several ranges along the coast (the Coast Ranges) and further into the continent (the Sierra Nevada, the Rocky Mountains, and the Cascade Mountains). In the east the Appalachian Mountains run. The highest mountain is McKinley (6 194 m). The highest volcano is Orizaba (5 747 m). There are also some lowlands: the Mississippi Lowland, the Preatlantic Lowland, the Premexican Lowland and the Central Plains. North America is rich in gold, copper, uranium, polymetallic ores, oil and gas.
4. Climate. The continent crosses all climatic belts but equatorial. The greater part of it is in temperate zone. In arctic zone winters are severe with heavy snow-falls and violent snow storms. The summer here is cool. The polar nights last for 5 months. Most territories are covered with ice.
The oceanic currents influence the climate mostly in the coastal regions. The warm North Pacific current brings many rainfalls and high to. The cold Californian Current cools and dries the territory of California. The tropical climatic belt is divided into two regions: tropical deserts and tropical wet climate. In subequatorial climatic belt the to is high all year round and there are many rains in summer.
Climatic Belts. (Laboratory Work).
5. Inland Waters. There are many rivers in North America. They are rain-fed and snow-fed. The main river in North America is the Mississippi (6 420 km). It is the biggest river in the continent and one of the largest rivers in the world. It rises in the middle of the continent and flows south across the plain into the Gulf of Mexico. Its the longest tributary is the Missouri (4 740 km). Other tributaries are the Ohio (1 580 km) and the Arkansas (2 410 km). There are also some other rivers, which fall into the Atlantic Ocean: the Colorado (2 333 km) and the Rio-Grande (3 033 km). Five Great Lakes have an outlet to the Atlantic Ocean through the rapid and deep St. Laurence River (3 057 km). They are: Lake Superior (393 m deep), Lake Michigan (281 m deep), Lake Ontario (236 m deep), Lake Huron (208 m deep) and Lake Erie (64 m deep). Lake Superior is the largest fresh-water lake in the world (over 80 000 sq.km). Lake Erie and Lake Ontario are connected by the Niagara River. Throwing its water from the height of 50 m., it forms the Niagara Falls. Many tourists come to see it. A number of rivers fall into the Arctic Ocean. They are mostly snow-fed. The biggest among them is the Mackenzie River (5 472 km). In the north of the continent there are some lakes. They are: the Great Slave Lake (614 m deep), the Great Bear Lake (137 m deep), Athabasca (60 m deep) and Winnipeg (18 m deep). Rivers of the Pacific Ocean basin are short, rapid and full of water. They are: the Columbia (1 953 km) and the Yukon (2 897 km). In the Cordilleras there is a big lake with salty water in it – the Great Salt Lake (14 m deep).
6. Natural Zones.
6.Population. More than 460 million people live in North America. The average density of population is 15 persons to a square km. The highest density (200 persons to a sq km) is near the Great Lakes, in the eastern part of the continent and on the islands in the Caribbean Sea. Less populated territories are in the north of the continent. Greenland is unpopulated. The native population of North America consists of the Indians and the Eskimos. The majority of people are descendants of settlers from Europe. There are also many Negroes in North America. The greater part of the continent is occupied by three big countries Canada, the USA and Mexico. There are also many small countries in Central America. Home task: choose any country and make a reportaccording to the plan (see page 18).
Cuba is rather a small country of North America, which is situated on the biggest island of the Caribbean Sea and on some small groups of nearby islands. The total area of the country is 110 860 thousand sq km. It is a republic, where state power belongs to the State Committee. The state language is Spanish. The population of Cuba is 11 million 184 thousand people. The climate here is subtropical. The average to is +25 o C. Rains last from May until October. The amount of rainfalls here is rather high – 1 400 mm a year.
The capital of Cuba is Havana. It is its political and cultural centre. Over 2.5 million people live in the city. Havana is full of interesting places to visit. You can find museums, old castles and churches here. Cuba is well known for its comfortable hotels and beautiful beaches. There are many places to swim and to have a rest on a hot and sunny day.
Eurasia. 1.Geographical Position.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2016-09-20; просмотров: 593; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.219.140.227 (0.324 с.) |
 2.The Discovery of Africa.
2.The Discovery of Africa. In the 15-th century the Portuguese sailors went around the continent in search of the route to India. In 1498 Vasco da Gama (1460 -1524) and his sailors reached the southern coasts of Africa. Since the 16-th century the Europeans began to take away slaves from Africa.
In the 15-th century the Portuguese sailors went around the continent in search of the route to India. In 1498 Vasco da Gama (1460 -1524) and his sailors reached the southern coasts of Africa. Since the 16-th century the Europeans began to take away slaves from Africa.
 The network of rivers depends on relief, temperature and rainfalls. African rivers are mainly rain-fed and overflow in the rainy season. Most rivers carry their waters into the Atlantic Ocean. There are some big rivers: the Nile (6 671 km), the Congo (4 320 km), the Niger (4 160 km), the Zambezi (2 660 km).
The network of rivers depends on relief, temperature and rainfalls. African rivers are mainly rain-fed and overflow in the rainy season. Most rivers carry their waters into the Atlantic Ocean. There are some big rivers: the Nile (6 671 km), the Congo (4 320 km), the Niger (4 160 km), the Zambezi (2 660 km).

 plan.
plan. Tanzania.
Tanzania. The government rules the country. The head of the country is the president. It is divided into 25 regions. There are two state languages in Tanzania: English and Swahili. Nearly 99 % of the population consists of African people. Other people come from European countries.
The government rules the country. The head of the country is the president. It is divided into 25 regions. There are two state languages in Tanzania: English and Swahili. Nearly 99 % of the population consists of African people. Other people come from European countries. One can find rare forests, savannahs and wet equatorial forests in Tanzania. Many red trees grow here. Animal world in the country is very rich. Antelopes, zebras, elephants, hippopotamus, rhinoceros, giraffes, lions, leopards and different kinds of monkeys live here. The biggest lakes as Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika and Lake Nyasa are situated in the country.
One can find rare forests, savannahs and wet equatorial forests in Tanzania. Many red trees grow here. Animal world in the country is very rich. Antelopes, zebras, elephants, hippopotamus, rhinoceros, giraffes, lions, leopards and different kinds of monkeys live here. The biggest lakes as Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika and Lake Nyasa are situated in the country.

 The great English explorer and sailor James Cook (1728 - 1779) discovered the eastern coast of Australia in the 18-th century. During his voyage around the world he reached the new continent, proved that New Zealand was an island and discovered the Great Barrier Reef. Some time later, when gold was found in Australia, England announced the continent its colony.
The great English explorer and sailor James Cook (1728 - 1779) discovered the eastern coast of Australia in the 18-th century. During his voyage around the world he reached the new continent, proved that New Zealand was an island and discovered the Great Barrier Reef. Some time later, when gold was found in Australia, England announced the continent its colony.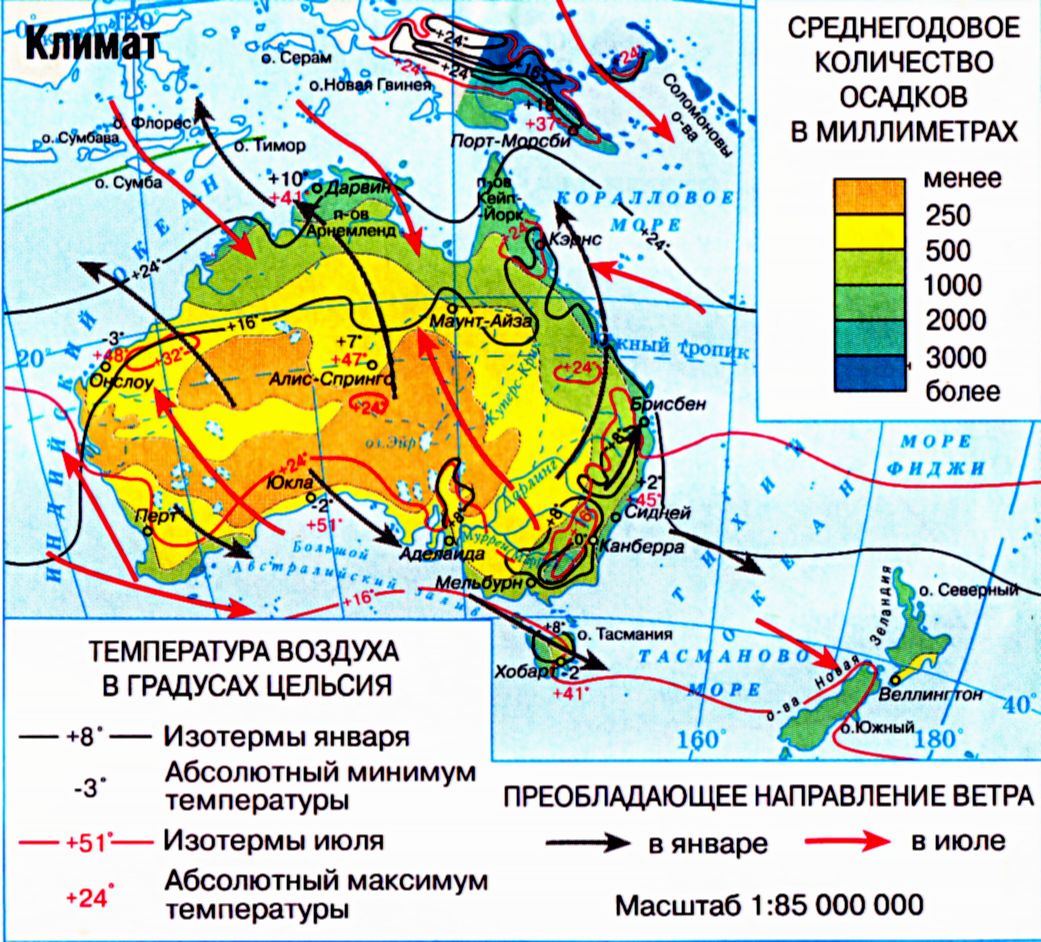 Australia is the only continent without active volcanoes. It is rich in coal, iron and polymetallic ores, gold and uranium.
Australia is the only continent without active volcanoes. It is rich in coal, iron and polymetallic ores, gold and uranium.




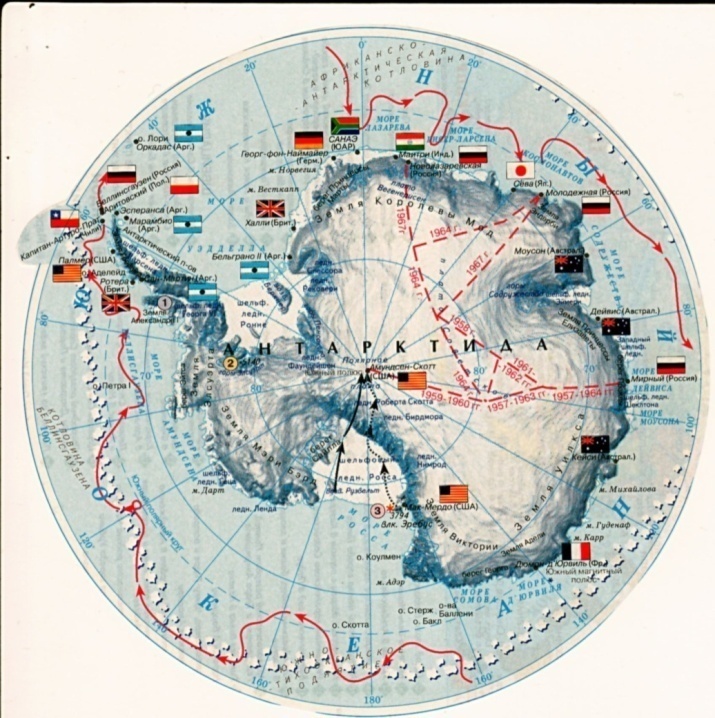
 There are some lands discovered and named by different people. They are Land Victoria, the Wilkes Land, the Mary Berd Land, the Ellsworth Land, the Alexander I Land, the Queen of Fashion Land, the Antarctic Peninsula and the Southern Polar Plato.
There are some lands discovered and named by different people. They are Land Victoria, the Wilkes Land, the Mary Berd Land, the Ellsworth Land, the Alexander I Land, the Queen of Fashion Land, the Antarctic Peninsula and the Southern Polar Plato.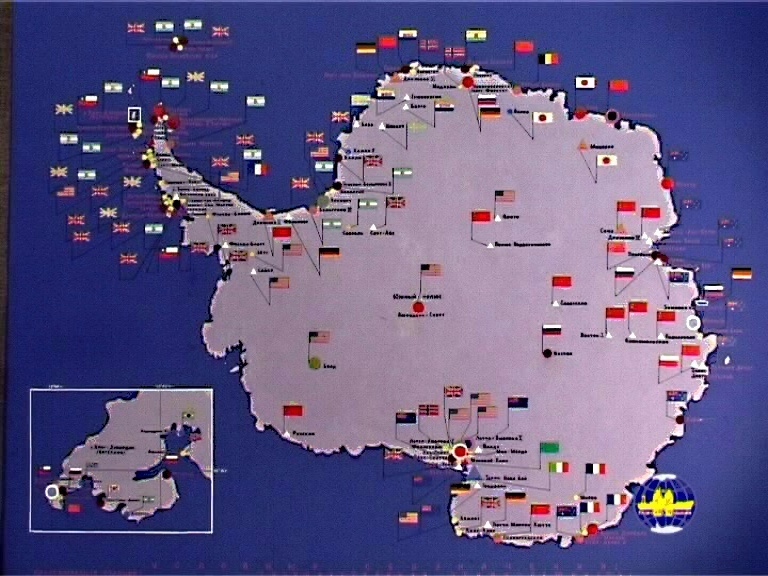 Among the American explorers of Antarctica, we can mention Charles Wilkes (1798-1877). He explored the coasts of the continent and discovered a new land called after him. Lincoln Ellsworth (1880-1951) was an American engineer and a pilot. He flew over Antarctica in 1935 and discovered a lot of unknown lands. One of them was called after him.
Among the American explorers of Antarctica, we can mention Charles Wilkes (1798-1877). He explored the coasts of the continent and discovered a new land called after him. Lincoln Ellsworth (1880-1951) was an American engineer and a pilot. He flew over Antarctica in 1935 and discovered a lot of unknown lands. One of them was called after him. 2. Climate.
2. Climate.
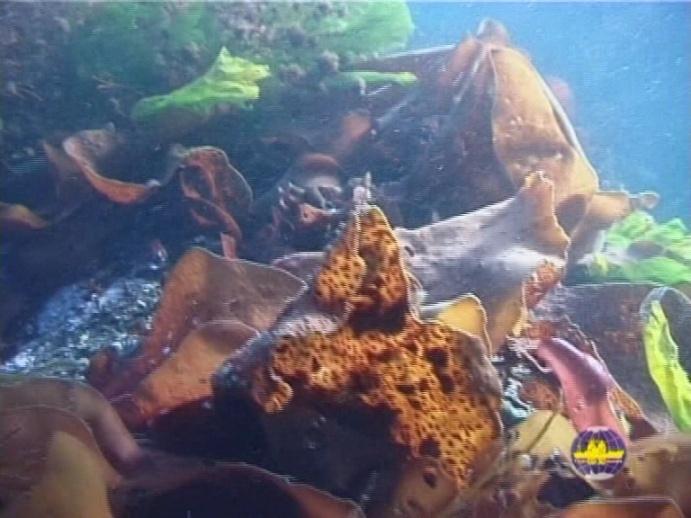
 In the water of the oceans and seas around Antarctica life exists too. Here you can find red, brown and green seaweeds. They grow rapidly in spring and summer, when water gets a little warmer and the sunbeams can reach the bottom. A lot of sea animals eating seaweeds live there. They are small fish, different crabs and starfish, bath-sponges and others. The water around Antarctica is also rich in plankton.
In the water of the oceans and seas around Antarctica life exists too. Here you can find red, brown and green seaweeds. They grow rapidly in spring and summer, when water gets a little warmer and the sunbeams can reach the bottom. A lot of sea animals eating seaweeds live there. They are small fish, different crabs and starfish, bath-sponges and others. The water around Antarctica is also rich in plankton.
 2. The Discovery of South America.
2. The Discovery of South America. America remained unknown to Europe until the end of the 15-th century. Of great importance at that time was trade with India and China. Some people thought that they could reach India by travelling west across the Atlantic Ocean. Christopher Columbus (1451 – 1506) was an experienced Spanish sailor, who asked the king of Spain to give him ships. He wanted to look for a new route to India. In 1492 he sailed across the Atlantic Ocean. They had been sailing for more than two months. At last they saw land which proved to be part of the Greater Antilles. He thought that it was India, so he called the native people of the islands Indians. He also discovered the Sargasso Sea and the Lesser Antilles.
America remained unknown to Europe until the end of the 15-th century. Of great importance at that time was trade with India and China. Some people thought that they could reach India by travelling west across the Atlantic Ocean. Christopher Columbus (1451 – 1506) was an experienced Spanish sailor, who asked the king of Spain to give him ships. He wanted to look for a new route to India. In 1492 he sailed across the Atlantic Ocean. They had been sailing for more than two months. At last they saw land which proved to be part of the Greater Antilles. He thought that it was India, so he called the native people of the islands Indians. He also discovered the Sargasso Sea and the Lesser Antilles.
 There are many big rivers in South America. Wet and warm climate, heavy rains and vast plains make the rivers full of water. They are mainly rain-fed.
There are many big rivers in South America. Wet and warm climate, heavy rains and vast plains make the rivers full of water. They are mainly rain-fed.

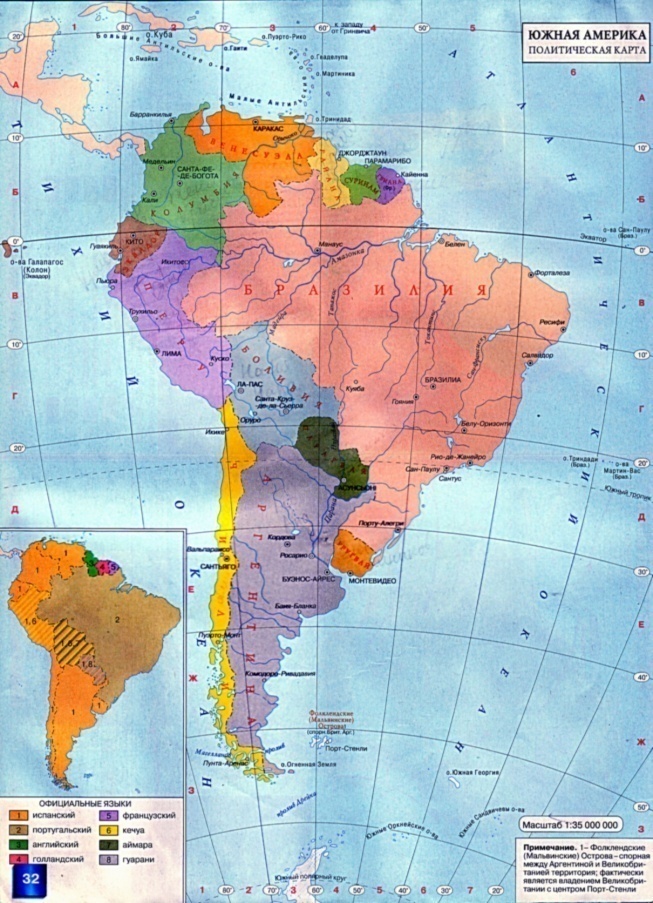
 Ecuador.
Ecuador.

 Vast territories of the country are covered with forests. In the forests there are bears, jaguars, skunks and other animals. You can also find different kinds of snakes, lizards and crocodiles here. Along the territory of the country many tributaries of the Amazon River flow. The Guas, the Napo, the Tigre and the Putumayo are among them.
Vast territories of the country are covered with forests. In the forests there are bears, jaguars, skunks and other animals. You can also find different kinds of snakes, lizards and crocodiles here. Along the territory of the country many tributaries of the Amazon River flow. The Guas, the Napo, the Tigre and the Putumayo are among them.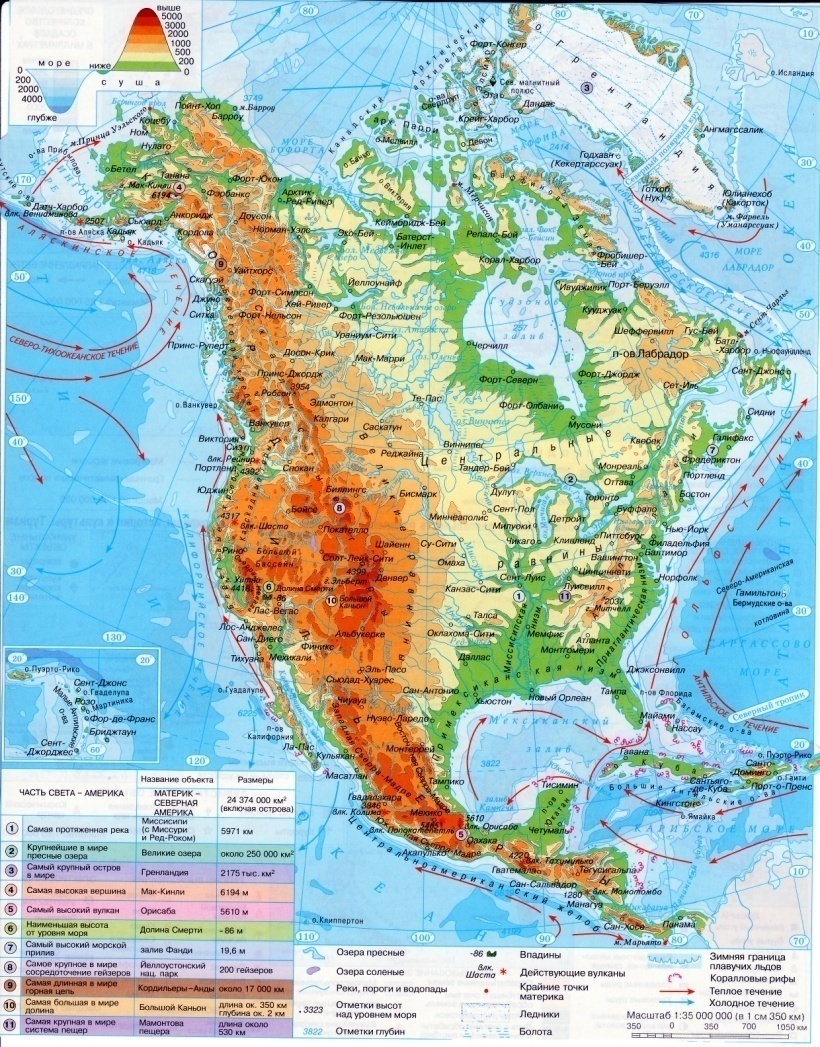
 2.The Discovery of North America.
2.The Discovery of North America. At the end of the 15-th century the English sailor John Cabot (1443 – 1498) came with his expeditions to the coasts of North America. He discovered Newfoundland, Labrador and eastern coast of the continent. The Spaniards explored Mexico and Central America in the 16-th century.
At the end of the 15-th century the English sailor John Cabot (1443 – 1498) came with his expeditions to the coasts of North America. He discovered Newfoundland, Labrador and eastern coast of the continent. The Spaniards explored Mexico and Central America in the 16-th century.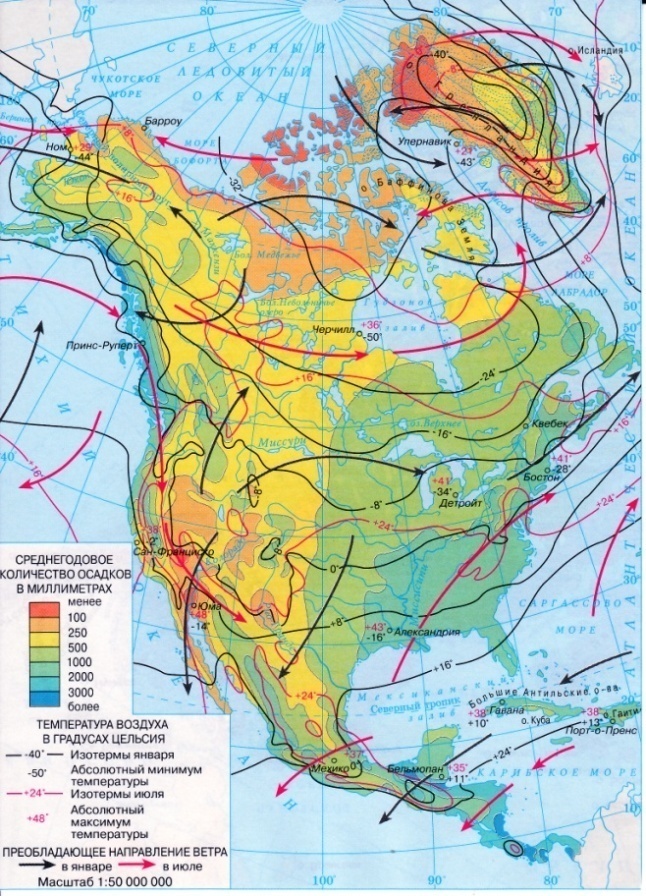 The climate of North America depends on winds, relief and oceanic currents. The Cordilleras make the climate of both sides of the continent different. The central part is occupied by the plains, so the tropical air masses move far to the north and the arctic air masses penetrate into the land to the Gulf of Mexico. That is why the weather here is changeable.
The climate of North America depends on winds, relief and oceanic currents. The Cordilleras make the climate of both sides of the continent different. The central part is occupied by the plains, so the tropical air masses move far to the north and the arctic air masses penetrate into the land to the Gulf of Mexico. That is why the weather here is changeable.




 Cuba.
Cuba. The climate is very good for the vegetation here. There are many tropical plants in Cuba. You can find 30 kinds of different palms on the islands of the country. Red-trees, sandals, poplars and pines also grow in the forests of Cuba. Some parts of the country are covered with grassy savannahs. Great amount of bats live here. You can find here over 300 kinds of birds, among which there are many parrots, flamingoes and hummingbirds. Over 700 kinds of fish and other sea animals live in the nearby waters of Cuba.
The climate is very good for the vegetation here. There are many tropical plants in Cuba. You can find 30 kinds of different palms on the islands of the country. Red-trees, sandals, poplars and pines also grow in the forests of Cuba. Some parts of the country are covered with grassy savannahs. Great amount of bats live here. You can find here over 300 kinds of birds, among which there are many parrots, flamingoes and hummingbirds. Over 700 kinds of fish and other sea animals live in the nearby waters of Cuba.





