
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
I. Define the meaning of the following parts of the predicate. Use the verb «делать» in the appropriate form instead of «х».Стр 1 из 24Следующая ⇒
ПРЕДИСЛОВИЕ В основу пособия положена модульная технология формирования лексико-грамматических навыков и развития умения читать англоязычную литературу. Такой подход предполагает тщательный отбор языкового материала, объединение логически связанных относительно самостоятельных частей в модули с последующим выделением дифференциальных признаков и созданием адекватных упражнений, что находит свое отражение в структуре четырёх модулей. Каждый из модулей включает: – схемы, в которых выделяются функции и значения логически связанных грамматических явлений на основе совокупности их инвариантных дифференциальных признаков, помогающих установить сходство и различие изучаемых явлений. Роль этих признаков велика, т.к. понимание речи при зрительном восприятии затрудняется отсутствием звуковых пауз, логического ударения, интонации, смыслового членения; – дифференцировочные упражнения на уровне абстракции, где лексические единицы заменены символом «х», к которому присоединяется дифференциальный признак, что позволяет чётко видеть изучаемую модель; – дифференцировочные упражнения на уровне разрозненных предложений с включением оппозиционного противопоставления интерферирующих грамматических явлений; – речевые упражнения на уровне текстов, предназначенные для развития умения читать и понимать литературу по профилю вуза (изучающее, ознакомительное, просмотровое, поисковое чтение, реферирование и аннотирование); – итоговые тесты. В пособие включены следующие модули: 1) глагол-сказуемое; 2) расширение простого повествовательного предложения и его структура; 3) сложное предложение; 4) инфинитивные и причастные обороты. В пособии модули расположены по принципу доминантности. Первым изучается модуль «глагол-сказуемое». Это объясняется ролью сказуемого как организующего центра предложения, подчиняющего себе остальные члены предложения. Соблюдается принцип преемственности, т.е. в каждый последующий модуль включаются грамматические явления, изученные в предыдущем, что способствует их лучшему распознаванию и пониманию. МОДУЛЬ 1 ГЛАГОЛ-СКАЗУЕМОЕ THE PREDICATE Исходные структурные элементы сказуемого
1Символ «x» обозначает любое незнакомое английское слово. 23-я форма неправильного глагола. Список основных неправильных глаголов находится в конце пособия. Признаки сказуемого в форме настоящего (Present Simple) И прошедшего (Past Simple) времени действительного залога
12-я форма неправильного глагола. Список основных неправильных глаголов находится в конце пособия. X. Answer the questions given in the text. XI. Translate passage 1 of the text. XIV. Translate passage 1 into Russian. Сказуемое с глаголом have. I. Compare points 2 and 3 of the table. Define their similarities and differences. Сказуемое с глаголом be Сказуемое с глаголом do. Личные формы глагола Активный залог Active Voice Worries about Internet Use 1. A recent survey into Internet use has thrown up some worrying results. The Stanford University survey asked respondents to answer a number of questions about their Internet use. It asked how much time they spent on the Internet and whether Internet use had affected the amount of time they spent with family and friends. 2. The answers were interesting but not unexpected. Two-thirds of the people surveyed responded that they still spend fewer than five hours a week on the Internet. The survey concludes that the behaviour of these people has changedlittle. However, a quarter of those people who use the Internet for more than five hours a week claimed that they spend less time with their family and friends. 3. Professor of Political Science at Stanford, Norman Nie, tells us that we are moving from a world where we know and see neighbours and friends to one where interaction takes place at a distance. It seems that the results of the survey prove that the Internet is turning people into solitary beings who can’t be bothered to call their mother on her birthday.
XI. Answer the following questions: 1. What survey did the Stanford University carry out? 2. What results were achieved? 3. What are the worries about Internet use? 4. Why do people feel lonelier today than they used to? 5. How much time do you spend surfing the Internet? Is there anything that you want to change? Страдательный залог Passive Voice Страдательный залог показывает, что действие направлено на предмет или лицо, выраженное подлежащим.
И русском языках
А. Предлог, стоящий после глагола в страдательном залоге и не относящийся к следующим за ним словам, при переводе на русский язык ставится перед тем словом, которое в английском предложении является подлежащим:
Запомните значения следующих глаголов с предлогами:
Computers Then and Now 1. The world first electronic computer was built at the University of Pennsylvania in 1946, although computer-like machine was built in the 19th century. Computers were sold commercially for the first time in the 1950s, and a lot of progress has been made since then. Computers are now much smaller and more powerful, and they can be bought much more cheaply. 2. Computers are used in many fields – in education, medicine, science, for example. They can be used to forecast the weather or to control robots which make cars. A lot of difficult calculations can be done very quickly on a computer. 3. A computer can’t think – it must be told exactly what to do. And they don’t make mistakes. Stories are heard sometimes about computers paying people much money or sending them bills for things they don’t buy. These mistakes are made by the programmers. Some years ago, a computer-controlled rocket belonging to the USA went out of control and had to be destroyed. The accident was caused by a small mistake in one line of the programme. This mistake cost the USA $ 18 million. 4. Progress is being made all the time. Today people know more about computers then they used to. And many believe we can look forward to the day when even our household jobs like cleaning will be done by computer-controlled robots.
Predicates with modal verbs Значения модальных глаголов
I. Compare the modal verbs below. Explain their differences. Can-may; can-could; can-might; may-might; may-could; must-may; should-can; must-should; could-should;can-must; might-could; should-may; must-might. Итоговый тест I. Подберите слово, близкое по значению данному:
II. Заполните пропуски в тексте подходящим по смыслу словом.
a) displays; b) provided; c) converts; d) accessed; e) combines; f) referred to.
World Wide Web (WWW), computer-based network of information resources that (5) ___ text and multimedia. The information on the World Wide Web can be (6) ___ and searched through the Internet, a global computer network. The World Wide Web is often (7) ___ simply as «the Web». The Web started to become a popular resource after 1993 when the first widely distributed browser (8) ___ a convenient way to access a variety of information on the Internet.
VII. Прочитайте текст. Затем изучите утверждения после текста и отметьте: T (true), если утверждение верное; F (false), если утверждение неверное; N (no information), если в тексте об этом не говорится. Our current «age of technology» is the result of many brilliant inventions and discoveries, but it is our ability to transmit information, and the media we use to do it, that is perhaps most responsible for its evolution. Progressing from the copper wire of a century ago to today’s fiber optic cable, our increasing ability to transmit more information, more quickly and over longer distances has expanded the boundaries of our technological development in all areas. Today’s low-loss glass fiber optic cable offers almost unlimited bandwidth and unique advantages over all previously developed transmission media. The basic point-to-point fiber optic transmission system consists of three basic elements: the optical transmitter, the fiber optic cable and the optical receiver. 25. Today’s low-loss glass fiber optic cable offers unique advantages over all transmission media. 26. Fiber optic cable is similar to electrical cable in its construction. 27. The basic point-to-point fiber optic transmission system consists of three basic elements: the optical transmitter, the copper wire and the optical receiver. 28. Many brilliant inventions and discoveries are most responsible for the evolution. МОДУЛЬ 2 Post Office Protocol 1. POP is a message-retrieval protocol used by many PC mail clients to get messages from a server, typically your ISP’s mail server. It only allows you to download all messages in your mailbox at once. It works in «pull» mode: the receiving PC initiates the connection. PC-based POP3 mail clients can do this automatically at a preset interval. When you use your Web mail account to access a POP3 mailbox, the mail server opens a connection to the POP3 server just as a PC-based application would. The messages are then copied into your Web mailbox and read via a browser.
2. Since POP3 downloads all the messages in your mailbox, there is an option to leave messages on the server. This does mean that you’ll get every message downloaded every time you connect to the server. If you don’t clean out your mailbox regularly, this could mean long downloads. Many Web mail systems won’t recognize messages you’ve already downloaded, so you’ll get duplicates of ones you haven’t deleted. Заменители артикля
I. In each line find the determiners of the noun and give their Russian equivalents.
II. Choose the word the translation of which is given at the beginning of each line.
III. Define the similarities and difference of the words given below:
Функции и значения one
I. Define the functions and meanings of one. Give the Russian equivalents of the following sentences. 1. The serving network is the one that is currently providing service in the area where the user has roamed. 2. This is one of the reasons why a user-friendly print-version of web pages is essential for good user experience. 3. Users don’t scan a web-page in a linear fashion, going sequentially from one site section to another one. 4. In nearlyevery paragraph, there is one idea that is more important than all the others. 5. The last experiments gave us much better results than did the previous ones. 6. Laser is one of the most sophisticated inventions of man. 7. One doesn’t have to prepare a new program each time you set a new function to a microprocessor-equipped robot.
II. Give the Russian equivalents of the following nouns, paying attention to the meanings of the words from which they are derived. Interactivity (interact – взаимодействовать), encoder (encode – кодировать), compression (compress – сжимать), innovation (innovate – вводить новшества, менять), conversion (convert – преобразовывать), expansion (expand – расширять), conduction (conduct – проводить). Прилагательные и наречия. Сравнительная степень
1 Односложные прилагательные/наречия; двусложные прилагательные, оканчивающиеся на -er, - ly, - e, - w/ двусложное наречие early. 2 Двусложные прилагательные (кроме тех, что указаны в сноске 1), многосложные прилагательные; двусложные наречия и наречия с суффиксом - ly.
Превосходная степень
1 Односложные прилагательные/наречия; двусложные прилагательные, оканчивающиеся на -er, - ly, - e, - w/ двусложное наречие early. 2 Двусложные прилагательные (кроме тех, что указаны в сноске 1), многосложные прилагательные; двусложные наречия и наречия с суффиксом -ly.
I. Find the adjectives and adverbs in the a) comparative degree and b) superlative degree. Name their features. Model these sentences. a) 1. X x x is more xly x. 2. One x x may x xly xer than x. 3. X x is for xer x and x x x. 4. More x x of a x x x is its x. 5. These xs are more x than those xs. b) 1. The x is the most x x x. 2. The x x the most x x of x. 3. The xest x in x x is x. 4. A x x the xest x to x x and x x. 5. Xs are most xly x.
II. In each line find the word-combination a) With an adjective or adverb in the comparative degree 1) a layer; more permanent; the most common; the server; 2) the disk controller; outer space; a thinner layer; a previous layer; 3) the common emitter circuit; a power amplifier; the most powerful computer; more detailed local forecasts; 4) the former computer; upper limit; laser diode; a thicker layer; 5) more easily installed; may easily gain access; relatively easy; d) very easy; 6) other devices; under increasing competition; supercomputer maker; more quickly replaced. b) With an adjective or adverb in the superlative degree: 1) most hard disks; the hardest materials; most materials; 2) the most heat-resistant materials; more computing power; most of the electron flow; 3) smaller electrical circuits; the earliest method; most research programs; 4) newer technology; most personal computers; the nearest telephone switching facility; 5) ever more powerful microcomputers; most notably; easily recognizable; most of the advances; 6) by most definitions; mostly mechanical; for most computational tasks; most widely used. III.Compare the words in bold type by form and meaning, define their similarities and differences.
1. a) The latter procedure is much more complicated than the former one. b) In the later evolution of multichannel fiber transmission systems, two distinct methods of multiplexing data have been introduced. c) Wi-Fi’s latest version is many times faster than DSL or cable connections. 2. a) Another common artificial intelligence application for multiprocessing was chess. b) Home burglar alarms, smoke detectors, and automobile alarms are three of the most common types of warning systems. c) Digital systems are much easier and smaller to design than comparable analogue circuits. This is one of the main reasons why digital systems are more common than analogue. d) Personal computers are now commonly equipped with dedicated video memory for holding high-resolution bit maps. 3. a) Wide-area networks connect computers and smaller networks to larger networks over greater geographic areas, including different continents. b) The largest wide-area network is the Internet. c) Organizations that have large amounts of printed information are working to transfer their information into databases. d) Although in principle these were general-purpose computers, they were still largely restricted to doing tough mathematical problems.
Сравнительные конструкции
I. Choose the sentences where the comparative constructions have the following meanings: a) такой же … как; b) не такой … как; с) чем; d) чем … тем. 1. Their operating system is considered by many people to be a better product than Microsoft’s. 2. The better you manage to provide users with a sense of visual hierarchy, the easier your content will be to perceive. 3. Operating systems are as old as electronic computers. 4. The better sense of orientation users have, the more trust they can develop toward the company the site represents. 5. There are several advantages in making computers as small as one can. 6. The bigger the mass, the bigger the weight of the body. 7. The new machines were smaller and less expensive than earlier models. 8. These engines are not so powerful as those motors. Предлоги 8.1 Предлоги, указывающие на местоположение 8.2 Предлоги, указывающие на время
Составные предлоги
Итоговый тест VII. Прочитайте текст. Затем изучите утверждения после текста и отметьте: T (true), если утверждение верное; F (false), если утверждение неверное; N (no information), если в тексте об этом не говорится. Compression reduces the size of video, data, image, and voice files. This decreases the amount of network capacity needed to transmit files. Compression increases throughput without changing the actual speed of the line. With compression, a song can be downloaded in seconds rather than in minutes because fewer bits will be sent. At the receiving end, compatible compression software or hardware re-creates the compressed chunks into close to or the same image or sound that was sent. Text is recreated exactly as it was before it was compressed so that numeric information or product information is not altered. However, when it is received, compression might re-create video and voice in varying degrees of lower video resolution or voice quality with acceptable, often barely noticeable, alterations. Compression used with text and facsimile often reduces the amount of data to be transmitted by removing white spaces and by abbreviating the most frequently appearing letters. For instance, repeated letters are abbreviated into 3-bit codes instead of 8-bit codes. In similar fashion, one method of video compression transmits only the changed image, not the same image over and over. In a video conference, nothing is transmitted after the initial image of a person until that person moves or speaks. Fixed objects such as walls, desks and background are not repeatedly transmitted. There are a number of standardized compression algorithms (mathematical formulae used to perform operations such as compression) that enable compressed text and video to be transmitted in a format that can be easily decompressed at the receiving end. The most frequently used compression protocols are: - various MPEG standards are used to compress and decompress audio and video. (MPEG stands for Moving Picture Experts group); - MP3 is used for downloading music files iPods; - Apple’s iPod uses Advanced Audio Coding (AAC); - Most Windows-based PCs have WinZip compression; - Zipit is installed on Macintosh computers running OS 10.x.x. 25. Compression greatly increases the actual speed of the transmission line. 26. Compressing makes the time for downloading a music file shorter reducing the number of bits to be sent. 27. In case of text compression, no change in the information is observed upon decompression. 28. Unlike compression, multiplexing does not alter the actual data sent. МОДУЛЬ 3 СЛОЖНОЕ ПРЕДЛОЖЕНИЕ The Compound Sentence
1 Иногда союз может отсутствовать. В таком случае между предложениями ставится точка с запятой.
The fastest desktop computers are called workstations, and they are used for scientific, engineering, or advanced business applications. Millions of people are simultaneously using the Net; the most efficient route between a given source and destination can change from moment to moment. Сочинительные союзы
Для соединения независимых предложений могут употребляться некоторые наречия:
The Complex Sentence
Усилительная конструкция
Многофункциональные слова Multifunctional Words
Broadband service 1. For most of the last 100 years the connection between the subscribers and their telephone exchange was copper twisted pair buried in the pavement or distributed overhead on poles. The bandwidth that copper provided was some 3kHz, limited by analog techniques. Thus, in the early 1990s, companies began to invest in alternative connections to the home to deliver digital-based services. 2. ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network). As you have seen the modem was a big breakthrough in computer communications converting digital information into an analog signal to travel through the public phone network. Yet, modems have a maximum speed of 56 Kbps and are limited by the quality of the analog connection. ISDN allows multiple digital channels to be operated simultaneously through the same regular copper-wire telephone lines (POTS) used for analog lines. Since the system is digital, it permits a much higher data transfer rate. Most recently, ISDN has largely been displaced by faster, less expensive, and easier to set up and maintain broadband services: DSL and cable modem. 3. DSL is a catchall name for all types of Digital Subscriber Lines that exploit unused spectrum capacity of copper telephone lines: new wiring is not necessarily required. DSLs use a special modem which is supplied by the company that offers DSL. The two types used mainly are: asymmetric (ADSL), for residential hookup, and symmetric (SDSL) for small businesses. DSLs allow the user to use the phone and fax lines while being connected to the Internet (except for SDSL) and to leave his Internet connection open 24 hours a day. As with ISDN, this connection works better when the user is closer to the provider’s central office. 4. Cable modem. A cable modem operates over cable TV lines, which provide greater bandwidth than POTS lines. Unlike the cable TV infrastructure, which broadcasts TV signals in just one direction (from the cable TV company to people’s homes), cable modems handle two-way transmission. For many home users, cable offers a fast, always-on Internet access at an affordable price. It has a number of disadvantages, too. Not all homes are yet wired for cable TV; since a user has to share bandwidth with other users, as with DSL, performance and speed will degrade the greater the number of subscribers in a given area. IX. Complete the table using the information from the text.
Бессоюзное подчинение Итоговый тест I. Выберите предложение(я), в которых that употребляется в функции союзного слова. 1. That same year Skype also became the foundation of the social network Facebook's video chat service. 2. Because of the digital nature of VoIP, call quality is normally much higher than that of a standard telephone. 3. Another advantage is that VoIP frequently costs less than standard telephone and long-distance service. 4. Wireless-enabled devices are able to connect to the Internet when they are near areas that have Wi-Fi access. VII. Прочитайте текст. Затем изучите утверждения после текста и отметьте: T (true), если утверждение верное; F (false), если утверждение неверное; N (no information), если в тексте об этом не говорится. A memory is just like a human brain: it is used to store data and instructions. Computer memory is the storage space in computer where data is to be processed and instructions required for processing are stored. The memory is divided into large number of small parts called cells, each cell has a unique address which varies from zero to memory size minus one. Memory is primarily of three types: Cache memory, Primary (main) memory, Secondary memory. Cache memory is a very high speed semiconductor memory which can speed up CPU. The parts of data and programs, which are most frequently used, are transferred from disk to cache memory by operating system, from where CPU can access them. The advantages of cache memory are as follows: it is faster than main memory; it consumes less access time as compared to main memory; it stores the program that can be executed within a short period of time; it stores data for temporary use. But there are some disadvantages: it has limited capacity and it is very expensive. Primary memory holds only those data and instructions that computer needs for current work. It has limited capacity and data is lost when power is switched off. Primary memory is generally made up of semiconductor device. These memories are not as fast as registers. The data and instruction required to be processed reside in main memory. It is divided into two subcategories RAM and ROM. Secondary memory is also known as external memory or non-volatile. It is slower than main memory and is used for storing data/information permanently. CPU does not access these memories directly, they are accessed via input-output routines. Contents of secondary memories are first transferred to main memory, and then CPU can access it.
25. Any type of memory is represented by cells, each having its proper address. 26. All three types of memory are non-volatile, i.e. the data is lost when the power is turned off. 27. Primary memory is considered to be the most efficient one. 28. Cache memory is said to be the fastest type of memory.
МОДУЛЬ 4 Инфинитивные обороты I. Find the attributive infinitive constructions. Give the Russian equivalents of the following structures with the infinitive. Use the word «делать» instead of the infinitive, «кто» instead of the subject. To 1 is, The x can 2, The x to be 3ed is, The x will 4, The x begins to 5, The x is the second to 6, The x was xed to 7, The x is the first to 8, The x xs the x to 9, The x to be 10
II. Find the attributive infinitive constructions. Give the Russian equivalents of the following parts of sentences: 1) an important issue to be discussed was; 2) there is a research to be held; 3) a new device model to be tested attracted; 4) there were the thesis figures to be calculated; 5) the project elements to be studied carefully are; 6) the engine to be repaired urgently was; 7) the research results to be covered at the conference were; 8) a new approach to be applied in the experiment found out; 9) the system bugs to be fixed were; 10) the chemical reactions to be evaluated are; 11) was the first to realize the difficulty of the situation; 12) is the second to invent this device. III. Find the attributive infinitive constructions, and give their features. Define the place and the sequence of the translation. 1. The plan of our work will be discussed at the meeting to be held on May 25. 2. The devices to be weighted were brought to the station. 3. The metal to be poured into a mold for casting may contract or expand on solidifying. 4. Не was the first to apply the new method of work. 5. Nearly all refrigerators to be used at home are based upon the principle that the rapid evaporation of a liquid or the expansion of a gas produces cooling. 6. For the experiment we need several electric devices to be connected in series. 7. He described the device to be usedin all modern systems. 8. The apparatus to be assembledis very complicated. 9. Lodygin was the first to inventthe electric lamp. 10. The measurements to be madeshould be accurate enough.
IV. Give the Russian equivalents, of the following groups of words and word combinations. Define their similarities and differences: a) to be in demand, to be a success, to be costly; b) is/are found, is/are expected, is/are taken, is/are reported; c) comparatively, daily, highly, likely/unlikely.
V. Match each English word from the left column with the correct Russian equivalent:
VI. Arrange in pairs the words with а) similar meaning, b) contrary meaning: a) requirements, vital, to have, to fabricate, to alloy, to calculate, to compute, essential, to manufacture, characteristics that are needed, to possess, to mix metals; b) inert, lighter, useful, unimportant, stronger, difficult, expensive, useless, simple, vital, active, cheap.
VII. In the text of task VIII find a word derived from the verb to resist. Give other derivatives of this verb.
VIII. Read the text and find the answer to the question: What metals used by ancient people were the first ones? Признаки распознавания Причастные обороты II. Find the participial constructions. Give the Russian equivalent of the following parts of sentences. Pay attention to the form of Participle I and Participle I Perfect in the attributive and adverbial participial constructions. a) 1. People investigating a lot; 2. Speaking at the conference I…; 3. When using this device he …; 4. While calculating the figures again I…; 5. Having learnt it he …; 6. Having increased the rate they …; 7. Being worked out by the specialists the program is…; 8. Having been repaired the engine began …. 9. Having been studied in detail the method was …; 10. Having been tested successfully the model. b) 1. People carrying out the research; 2. while calculating the figures; 3. the scientists conducting the experiment; 4. having attained the results; 5. IT specialists producing the final product; 6. the standard offering high-speed data; 7. early telegraphs using keyboards could produce tapes; 8. when drawing conclusions; 9. having discussed the questions; 10. while coming to an agreement. IV. Compare the form and meaning of the participles in the following attributive and adverbial constructions. Define their similarity and difference. Suggest whether this difference influences their meaning. 1. But further measurements usinga laser and looking for reflections showed that much of the ice is covered with a layer of dark material tens of centimeters thick. 2. This procedure was dropped, having given low yield of end products. 3. Having been carefully tested the device was put into operation. 4. Having determined the number of amperes and the number of volts, we can find the resistance of the coil by using Ohm’s law. 5. Having lost electrons, the atom of the metal is pacifier. 6. Having studied all the known elements he drew up a table of elements. 7. Having been employed in many industrial processes electronic computers show a notable example of progress contributing to the development of industry. 8. The source code of the malware program has become available online, allowing experts to analyze its complicated design. 9. Having changed the program the robot’s arm began to perform a new operation. 10. Having analyzed the situation he managed to carry out the experiment. Причастие I, II и герундий I. Point out Participle I and Perfect Participle in the passive form: a) 1ing, 2ed, having been 3ed, being 4ed, having 5ed; b) having been 6ed, 7ing, 8ed, having 9ed, being 10ed; c) being 11ed, having 12ed, 13ing, 14ed, having been 15ed; d) having 16ed, 17ing, 18ed, being 19ed, having been 20ed; e) 21ed, having been 22ed, being 23ed, having 24ed, 25ing; f) 26ing, having been 27ed, 28ed, being 29ed, having 30ed; g) 31ed, 32ing, having 33ed, having been 34ed, being 35ed. II. Find active and passive forms of the participles: a) having 1ed, have 2ed, being 3ed, be 4ed, has 5ed; b) had 6ed, 7ing, have been 8ed, being 9ed, having 10ed; c) has been 11ed, be 12ed, having been 13ed, had been 14ed, 15ing; d) had been 16ed, 17ed, having 18ed, has 19ed, is 20ed; e) are 21ed, be 22ed, being 23ed, having 24ed, have 25ed; f) was 26ed, to be 27ed, having been 28ed, 29ing, has 30ed; g) were 31ed, be 32ed, is 33ing, had 34ed, 35ed.
III. Using the tables on pages 104 and 105 in each line find the forms meaning: а) когда делается (p.104): 1ing, having 2ed, having been 3ed, being 4ed, be 5ed, have 6 ed, have been 7ed, being 8 ed, are 9 ed, 10ed; b) после того как был сделан (p.105): 1ing, having 2ed, having been 3ed, being 4ed, be 5ed, have 6ed, have been 7ed, having been 8ed, has been 9 ed, had been 10ed.
IV. Find Participle I and Perfect Participle in a) active, b) passive forms. Give their Russian equivalents: а) translating; having translated; having been translated; being translated writing; having written; having been written; being written; asking; having asked; having been asked; being asked; finishing; having finished; having been finished; being finished; b) receiving; having received; having been received; being received; doing, having done; having been done; being done; calling; having called; having been called; being called; learning; having learnt; having been learnt; being learnt.
Герундиальные обороты Герундий с относящимися к нему словами образует герундиальные обороты. Герундиального оборота
Герундиального оборота
III. Give the Russian equivalents of the following sentences. Pay attention to the translation of the gerundial constructions in the sentences. Find out the sentence without the gerundial construction. 1. In spite of not having the necessary expertise, the scientist made his great discovery. 2. These substances are alike in having high melting points. 3. Adding more turns makes the magnetic field stronger. 4. It is worthwhile considering more carefully the implication of the research results. 5. The scientist investigated the possibility of these rays being charged particles. 6. The analyst’s efficiency may be attributed to his having acquired, by constant training, the necessary technique. 7. To calculate the motion of an electron, we investigate the accompanying wave motion instead of using classical point mechanics. 8. The physicist’s being awarded the Nobel Prize soon became widely known. 9. Being appointed the head of the Department, Dr. Black started his work on atomic collisions. 10. The actual number of electrons depends upon the atom being considered. Итоговый тест VII. Прочитайте текст. Затем изучите утверждения после текста и отметьте: T (true), если утверждение верное; F (false), если утверждение неверное; N (no information), если в тексте об этом не говорится. A robot is a machine that gathers information about its environment and uses that information to follow instructions to do work. Imitating humans, robots also sense magnetic fields and ultrasonic waves. Robotic light sensors work by creating or changing an electric signal when light falls on them. When navigating, the robot sends out a beam of infrared light, which bounced off objects and returns to a light sensor of the robot. However, making 3D images requires large amounts of computer memory. Most robots have a microcomputer for «brains», which allows programming a lot of information. Neural networks are modelled after the human brain. Once trained, the neural net responds to an input with a likely output. Unlike rule-based systems, neural networks are incapable of giving definite answers. So, if robots eventually think like us, detect and express emotions, pursue their own interests and even make copies of themselves, drawing the line between machines and living things will be increasingly difficult. 25. When light falls on robots robotic light sensors start to function. 26. Most robots can «think», so it is possible to programme a great amount of information. 27. Neural networks are complicated systems used in the field of artificial intelligence. 28. The neural net of a robot responds to an input data without a likely output information. APPENDIX Словообразование Word Formation
Образование глаголов путём конверсии
Образование глаголов путём изменения места ударения
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-08; просмотров: 651; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 3.140.188.16 (0.26 с.) |
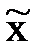 was, The x is too x to 11, To 12 is, The x may 13, The x shall 14, The x starts to 15, The x is the third to 16, The x is xed to 17, The x is the fourth to 18.
was, The x is too x to 11, To 12 is, The x may 13, The x shall 14, The x starts to 15, The x is the third to 16, The x is xed to 17, The x is the fourth to 18.


