
Заглавная страница Избранные статьи Случайная статья Познавательные статьи Новые добавления Обратная связь КАТЕГОРИИ: ТОП 10 на сайте Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрацииТехника нижней прямой подачи мяча. Франко-прусская война (причины и последствия) Организация работы процедурного кабинета Смысловое и механическое запоминание, их место и роль в усвоении знаний Коммуникативные барьеры и пути их преодоления Обработка изделий медицинского назначения многократного применения Образцы текста публицистического стиля Четыре типа изменения баланса Задачи с ответами для Всероссийской олимпиады по праву 
Мы поможем в написании ваших работ! ЗНАЕТЕ ЛИ ВЫ?
Влияние общества на человека
Приготовление дезинфицирующих растворов различной концентрации Практические работы по географии для 6 класса Организация работы процедурного кабинета Изменения в неживой природе осенью Уборка процедурного кабинета Сольфеджио. Все правила по сольфеджио Балочные системы. Определение реакций опор и моментов защемления |
Physical Properties of AminesСтр 1 из 4Следующая ⇒
Lecture 7 Nitrogen Compounds
2 Nomenclature of Amines 3 Physical Properties of Amines 4 Preparation of Amines
Organic nitrogen compounds: • amines, amino acids, amides and nitro compounds Amines are organic derivatives of ammonia. • We can think them as substituted ammonia molecules in which one, two or three of the ammonia hydrogens have been replaced by an organic group. • According to the number of organic groups (both alkyl or aryl groups) directly bonded to the nitrogen atom, amines are classified as:
Examples of 1° amines:
Examples of 2° amines:
Examples of 3° amines:
Addition of the fourth organic group to tertiary amine yields a quaternary ammonium ion
Aromatic amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in the ammonia are replaced by phenyl or substituted phenyl groups e.g.
If the substituent is present on the nitrogen, it is designated by the prefix N.
Nomenclature of Amines
e.g.
e.g.
Physical Properties of Amines • Lower members of amines are gases and have a characteristic ‘ammonia’ odour. • The higher members are liquids with a distinctive ‘fishy’ odour
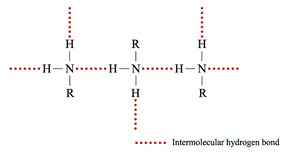
Boiling Point and Melting Point 1° or 2° amines can form strong hydrogen bonds with each other Þ the b.p. is higher than those of alkanes but lower than those of alcohols of comparable molecular masses ∵ O – H bond is more polar than N – H bond as oxygen is more electronegative Þ stronger hydrogen bonds are formed between alcohol molecules
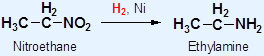
3° amines have lower b.p. and m.p. than 1° and 2° all hydrogen in 3° amines are replaced by organic groups Þ no hydrogen bond can be formed Density Molecular mass of amines Þ densities Solubility • The solubility of amines in water: ∵ The intermolecular hydrogen bonds formed between 2° or 3° amines and water molecules decrease • Amines are soluble in common organic solvents, e.g. hexane, ethanol and propanone Preparation of Amines Hydrogen reduces a nitro compounds to a 1° amine in the presence of nickel catalyst
Example:
Reduction of Nitriles Reaction with Hydrogen Hydrogen reduces a nitrile to a 1° amine in the presence of nickel catalyst
Example:
Reduction of Amides Hofmann Degradation • Amides with no substituent on the nitrogen react with Br2 in NaOH (or Cl2 in NaOH) to give amines
• The amines formed have one carbon less than the parent amides
Preparation of Phenylamine Reactions of Amines Basicity of Amines • Amines are far weaker bases than hydroxide ions but are stronger bases than water • The lone pair electrons on nitrogen atom can accept a proton from a water molecule Þ amines are basic
Amines dissolve in mineral acids such as HCl to form salts e.g.
Methylamine will partially dissociate into ions
pKb is used for convenience as Kb is small for weak bases
The basicity of amines is governed by the availability of the lone pair electrons on the nitrogen atom • Primary aliphatic amines are the most basic electron-releasing alkyl groups enhance the availability of the lone pair electrons on the nitrogen atom while ammonia does not • Aromatic amines are weaker bases than ammonia the lone pair electrons on the nitrogen atom are delocalized over the benzene ring making it less available to a proton
Acylation of amines • 1° and 2° amines react readily in cold with ethanoyl chloride or anhydride to form N -substituted amides Examples:
• 1° and 2° amines react with benzoyl chloride in the presence of alkalis to form N -substituted amides Examples:
N-nitrosoamines
Examples:
As Drugs Amine derivatives are commonly used as drugs such as painkillers (analgesics), transquillizers and antihistamines
• used to relieve pains • less harmful to the stomach compared with aspirin
• helps to relieve allergic disorders caused by cold, insect bites and stings • 3. Chlorpromazine • sedative effect without inducing sleep • used to relieve anxiety, excitement, restlessness and even metal disorders Контрольні питання до лекції 7. 1. Напишіть структурні формули сполук. Розташуйте сполуки за збільшенням їх основності. Дайте пояснення. П -хлоранілін, 2-бром-4-хлоранілін, о -толуїдин 2. Вкажіть правильну схему синтезу трет-бутанолу з ізобутилену. Напишіть реакції. А) 3. Встановити будову сполуки за брутто-формулою та продуктами хімічного перетворення: С7Н9N, з соляною кислотою утворює сіль, після послідовної взаємодії з нітритною кислотою і нітритом калію в присутності міді утворює п-нітротолуол. Напишіть реакції. 4. Запропонуйте схему синтезу м -метилфенолу з хлорбензолу 5. Lecture 7 Nitrogen Compounds
2 Nomenclature of Amines 3 Physical Properties of Amines 4 Preparation of Amines
Organic nitrogen compounds: • amines, amino acids, amides and nitro compounds Amines are organic derivatives of ammonia. • We can think them as substituted ammonia molecules in which one, two or three of the ammonia hydrogens have been replaced by an organic group. • According to the number of organic groups (both alkyl or aryl groups) directly bonded to the nitrogen atom, amines are classified as:
Examples of 1° amines:
Examples of 2° amines:
Examples of 3° amines:
Addition of the fourth organic group to tertiary amine yields a quaternary ammonium ion
Aromatic amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in the ammonia are replaced by phenyl or substituted phenyl groups e.g.
If the substituent is present on the nitrogen, it is designated by the prefix N.
Nomenclature of Amines
e.g.
e.g.
Physical Properties of Amines • Lower members of amines are gases and have a characteristic ‘ammonia’ odour. • The higher members are liquids with a distinctive ‘fishy’ odour
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 2017-02-07; просмотров: 293; Нарушение авторского права страницы; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! infopedia.su Все материалы представленные на сайте исключительно с целью ознакомления читателями и не преследуют коммерческих целей или нарушение авторских прав. Обратная связь - 18.118.140.108 (0.032 с.) |





















 The basic strength of amines is shown by the value of base dissociation constant (Kb)
The basic strength of amines is shown by the value of base dissociation constant (Kb)







 1. Acetaminophen (also known as paracetamol)
1. Acetaminophen (also known as paracetamol) 2. Chlorpheniramine
2. Chlorpheniramine present in some over the counter drugs such as Coricidin, Coltaline, Piriton and Dristan
present in some over the counter drugs such as Coricidin, Coltaline, Piriton and Dristan ; В)
; В)  ; С)
; С)  ; D)
; D)  .
. Запропонуйте схему синтезу барвника з азо- і діазокомпоненти. Назвіть сполуки.
Запропонуйте схему синтезу барвника з азо- і діазокомпоненти. Назвіть сполуки.


